Last updated: July 2025
GitLens provides multiple sidebars that extend the functionality of Visual Studio Code, making it easier to navigate and understand your Git repositories. These include:
- GitLens Inspect — View blame annotations, code lenses, and commit details.
- GitLens — Access features like commit history, branches, and remotes.
- Source Control — Integrates with GitLens to enhance the built-in source control panel.
Features marked with PRO require a trial or paid plan for use on privately hosted repos
Features marked with PREVIEW require a GitKraken Account, with access level based on your plan, e.g. Community, Pro, etc
Use the GitLens Sidebars
GitLens offers three sidebars in Visual Studio Code that enhance Git workflows with rich visualizations, insights, and collaboration tools.
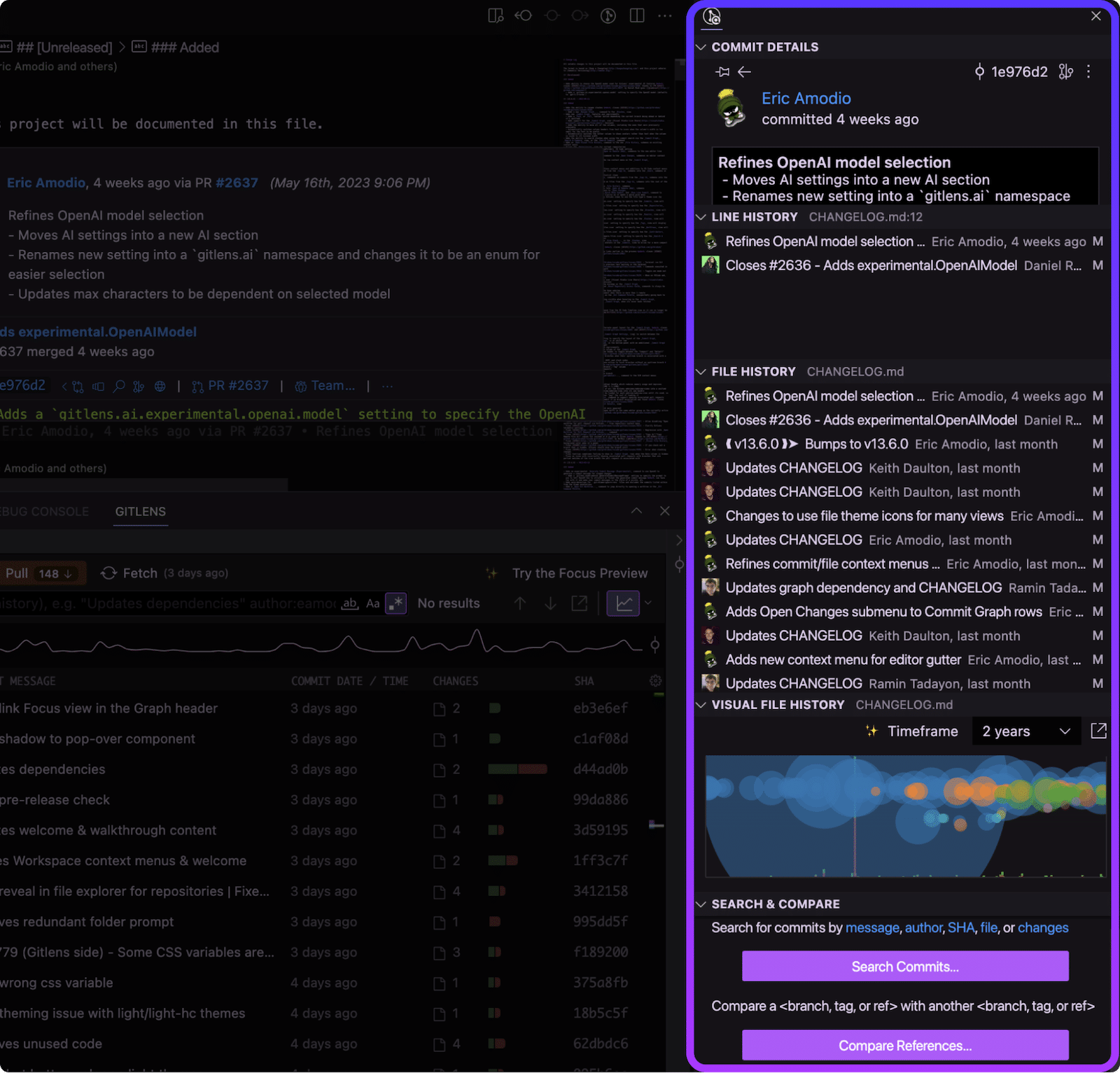
GitLens Inspect Sidebar
The GitLens Inspect sidebar provides contextual information about your current file, line, or repository activity. Use it to dive into commit details, history, and comparisons.
This sidebar includes:
- Commit Details
- Overview
- Line History
- File History
- Visual File History
- Search & Compare
GitLens Sidebar
The GitLens sidebar centralizes collaboration features and user tools, including GitKraken Workspaces and account settings.
This sidebar includes:
- Home View
- GitKraken Workspaces
- GitKraken Account
- Cloud Patches
PRO - Launchpad
PRO
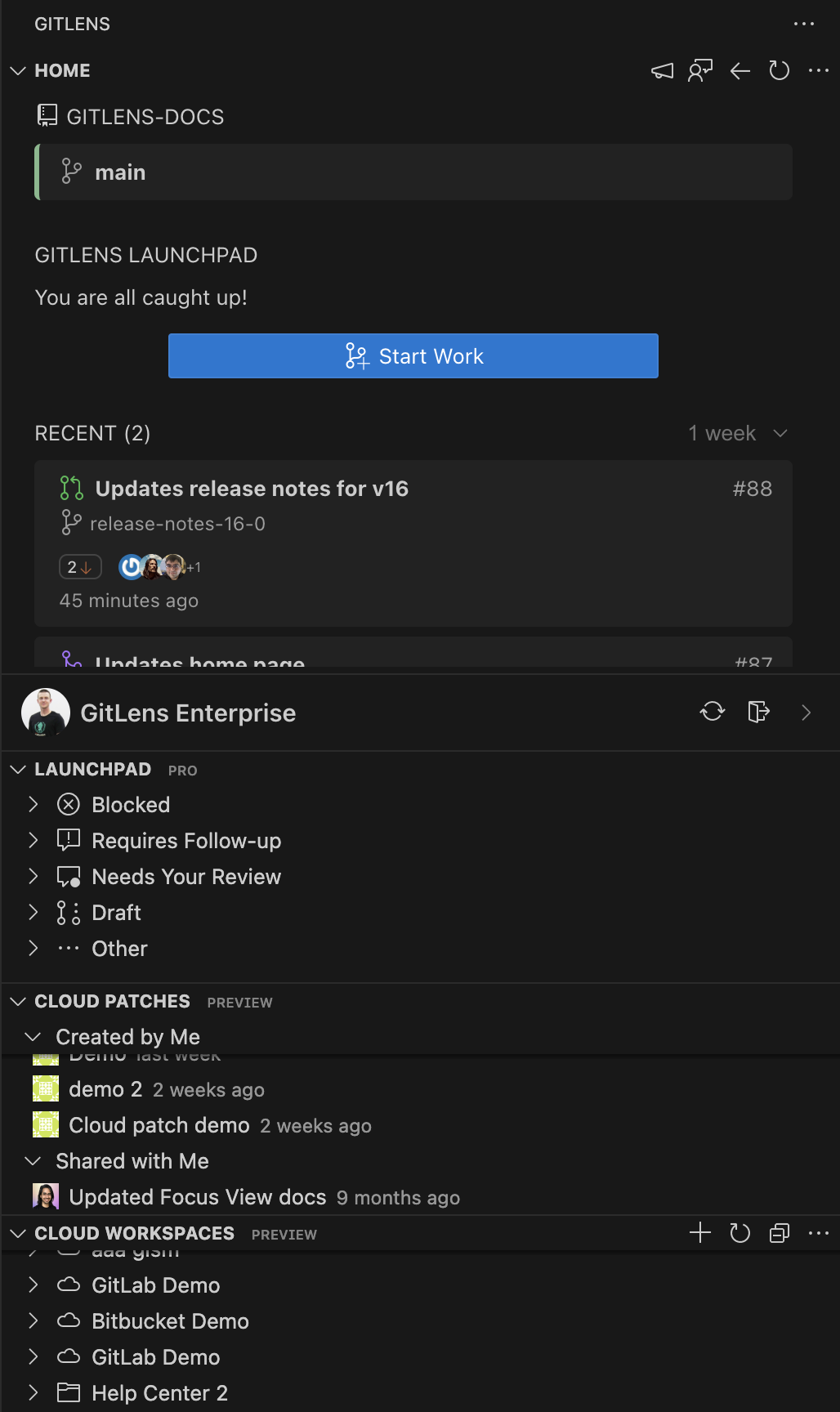
Home View Details
The Home View provides visibility into current tasks and recent activity. To get the most out of this view, connect your Git provider and issue integrations.
Sections include:
- REPOSITORY — Displays the active repository and branch, sync status, and actions for fetch/push/pull. Shows linked PRs or issues when available, or offers to start a new PR.
- LAUNCHPAD — Highlights pull requests needing review, those blocked, or ready to merge. Start new branches or worktrees tied to issues.
- RECENT — Quickly access recent branches, PRs, and worktrees.
Source Control Sidebar
The Source Control sidebar enhances VS Code’s native Git interface with additional GitLens-powered views.
This sidebar includes:
- Commits
- Branches
- Remotes
- Stashes
- Tags
- Worktrees
- Contributors
- Repositories
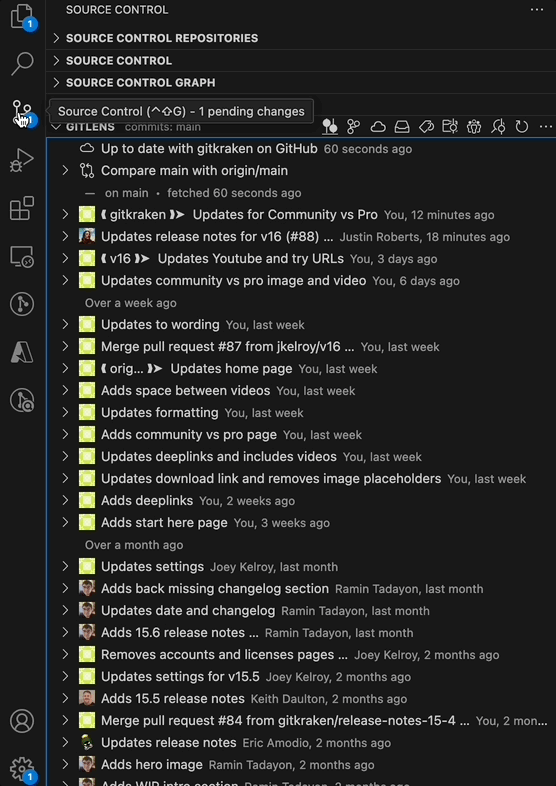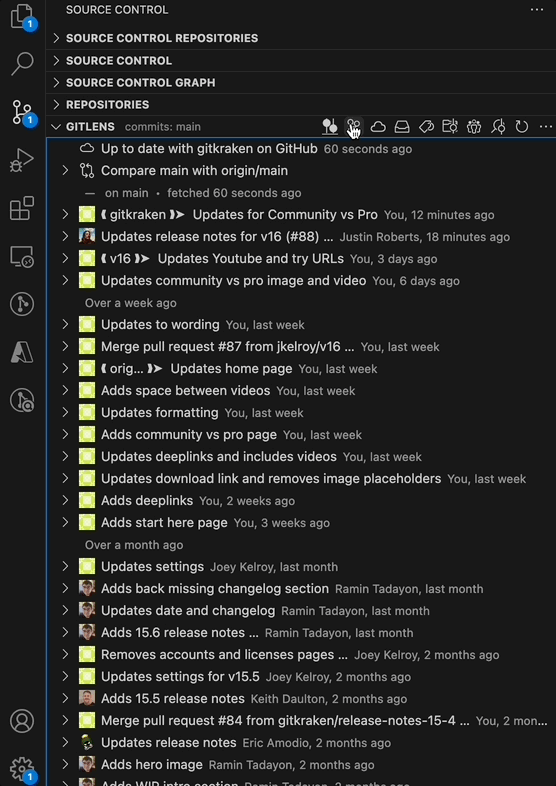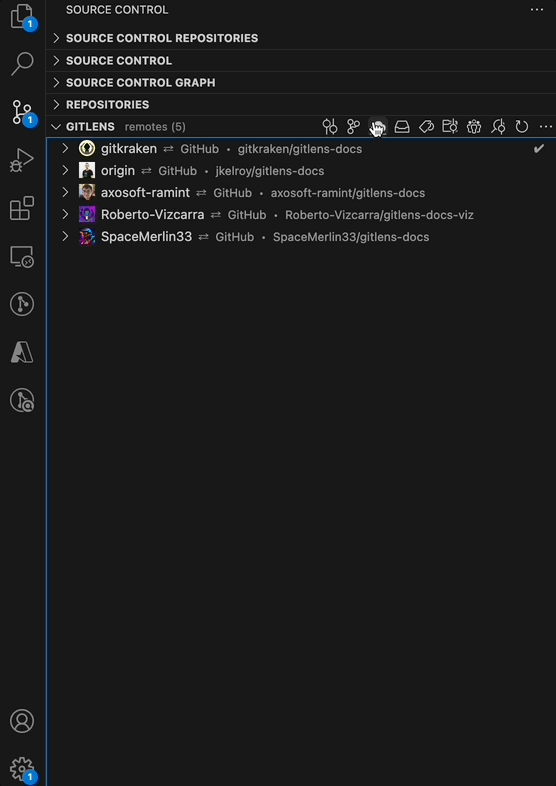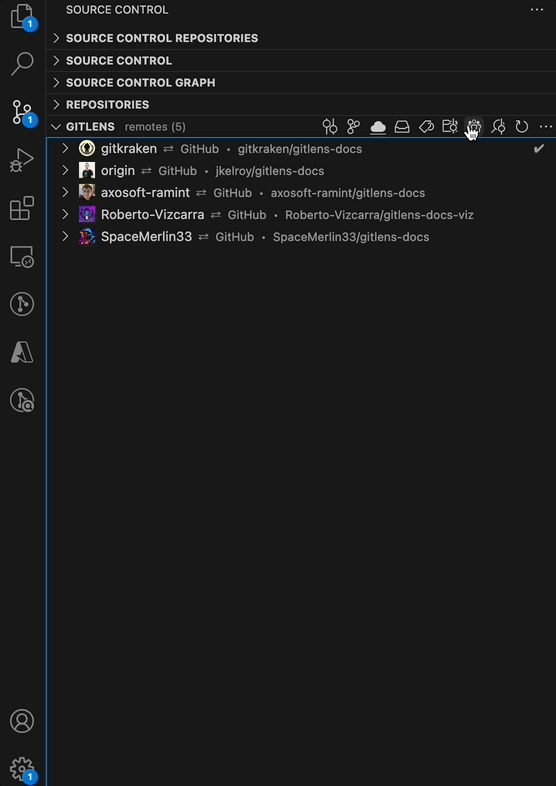
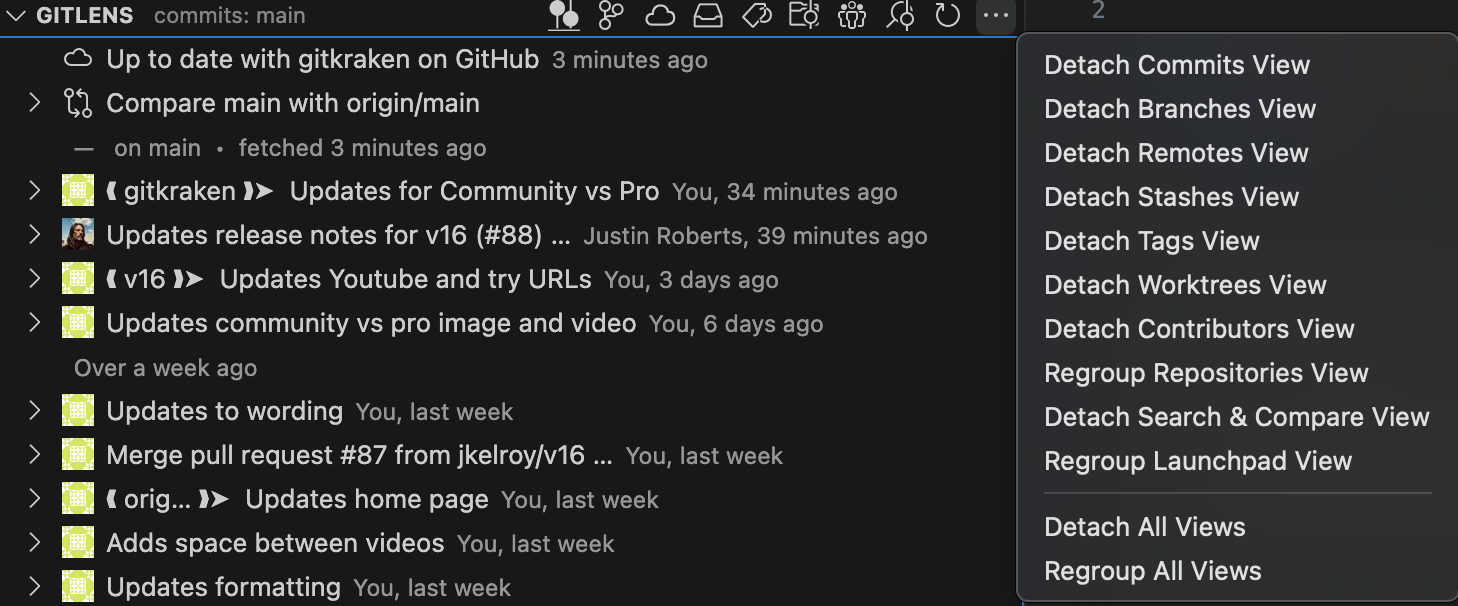
Views can be detached from the sidebar and moved or reattached using the ellipsis icon menu.
Move Views Between Sidebars
You can move any GitLens view between the GitLens Inspect, GitLens, and Source Control sidebars. To move a view, simply drag and drop it to the desired sidebar.
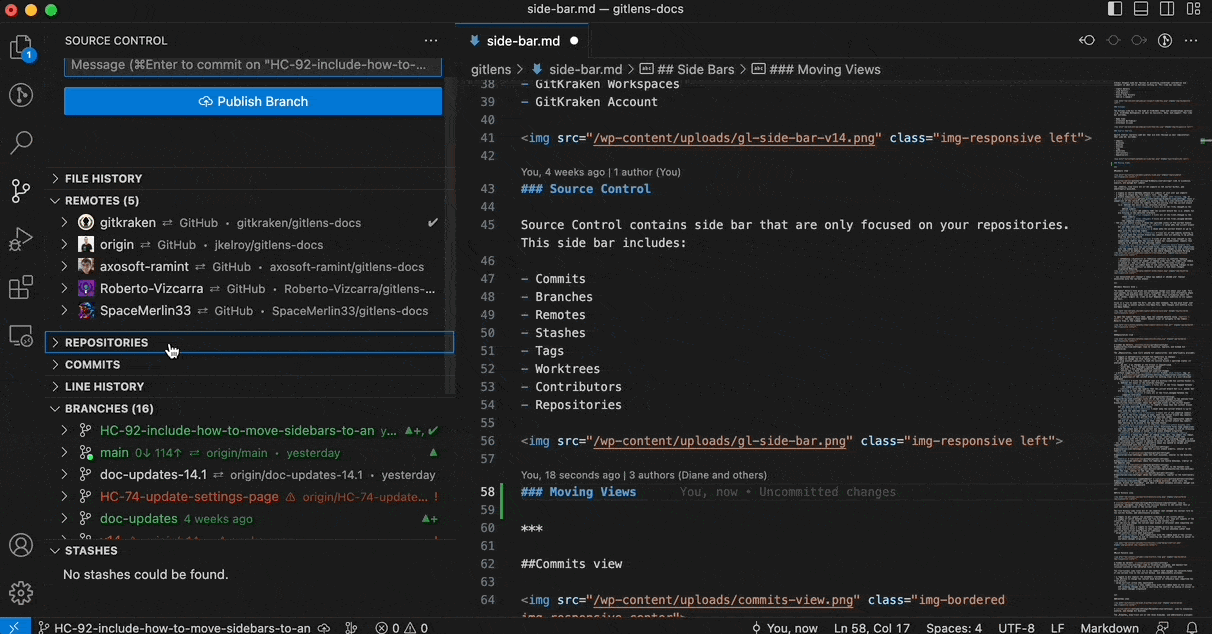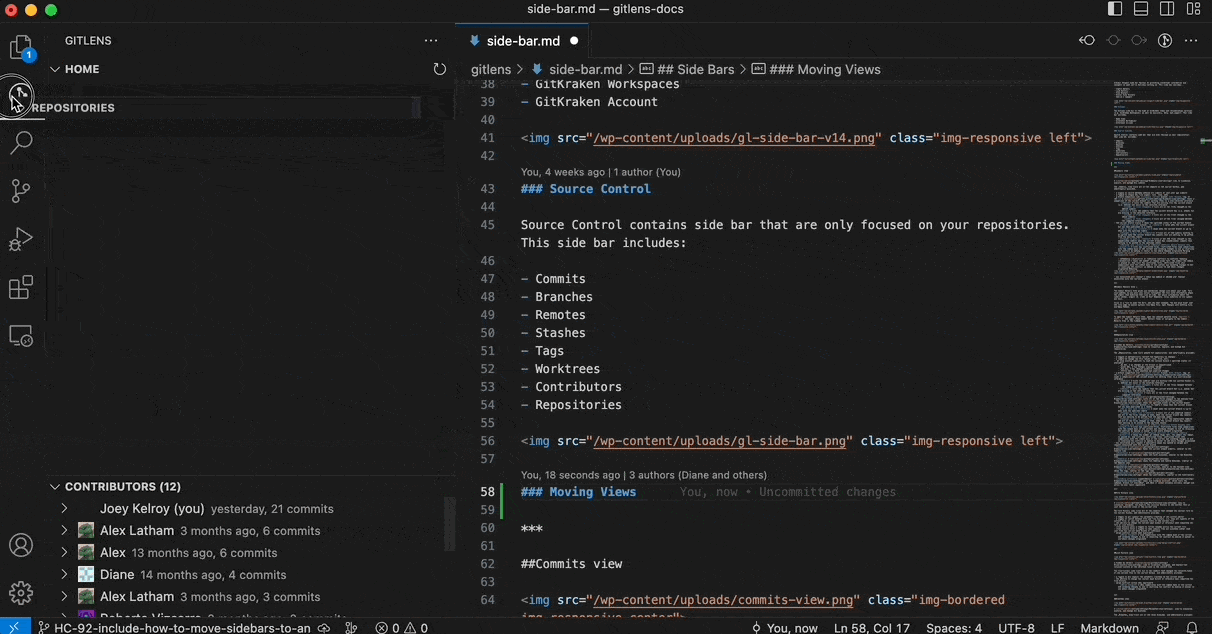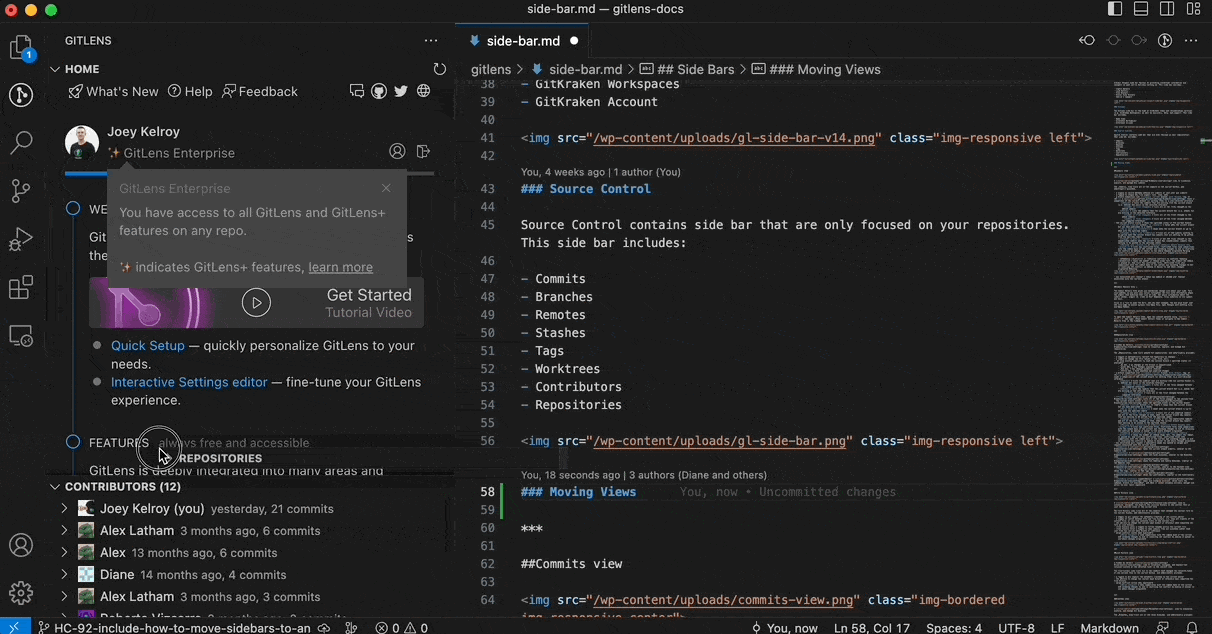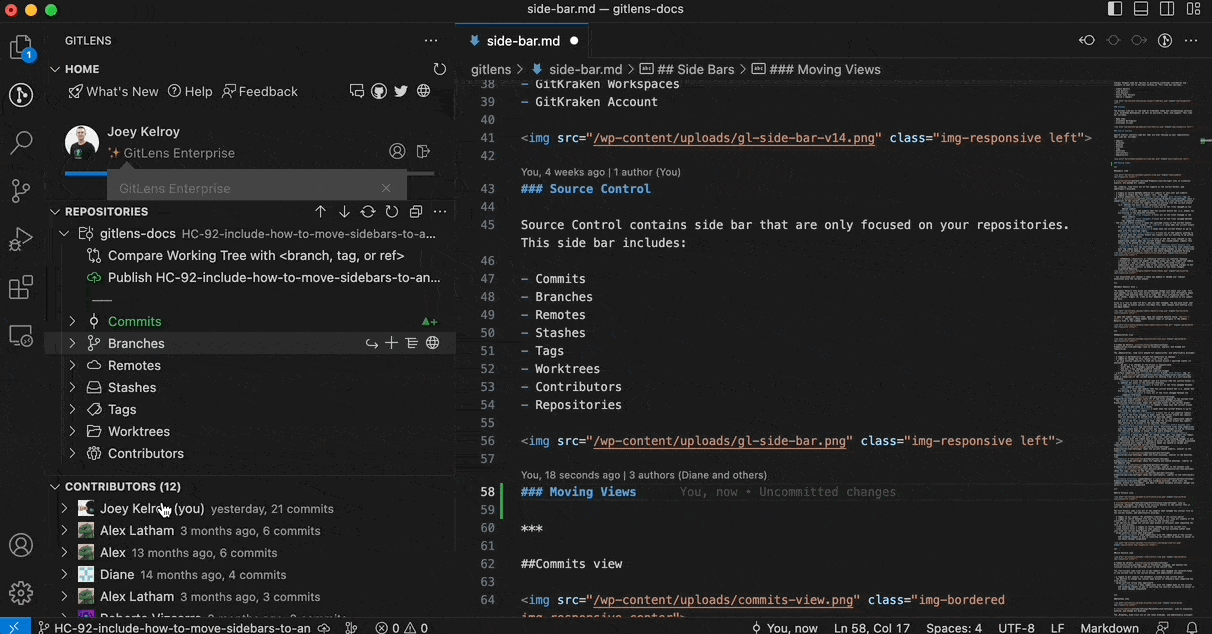
To restore the default layout, open the Command Palette (Cmd/Ctrl + Shift + P) and run:
View: Reset View Locations
Commits View
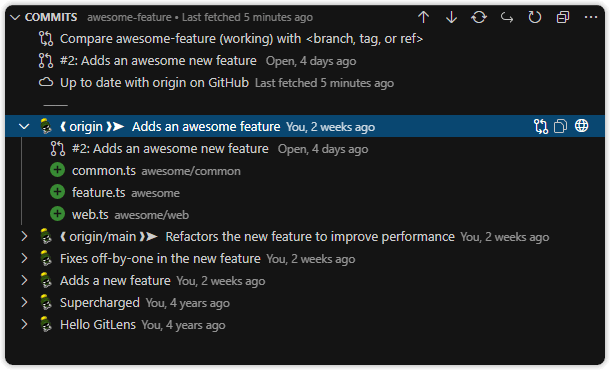
A customizable view to visualize, explore, and manage Git commits.
The Commits view displays all commits on the current branch. It also provides:
- A toggle to show all commits or only your own
- A toggle to switch file layout: list, tree, or auto
- A branch comparison tool — compare the current branch (or working tree) with a selected branch, tag, or ref
- Behind — shows commits missing from the current branch
- Ahead — shows commits present on the current branch but not on the selected reference
- Branch status with upstream info:
- Publish — option to publish if not yet pushed
- Up to date — when synced with remote
- Changes to pull — if commits are available on the remote
- Changes to push — if there are local unpublished commits
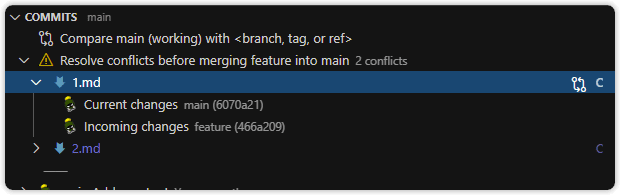
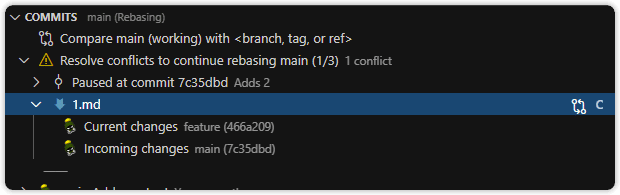
- Merging or rebasing — indicates in-progress merge or rebase actions and lists conflicted files
- Associated pull request — displays if a pull request is linked to the current branch
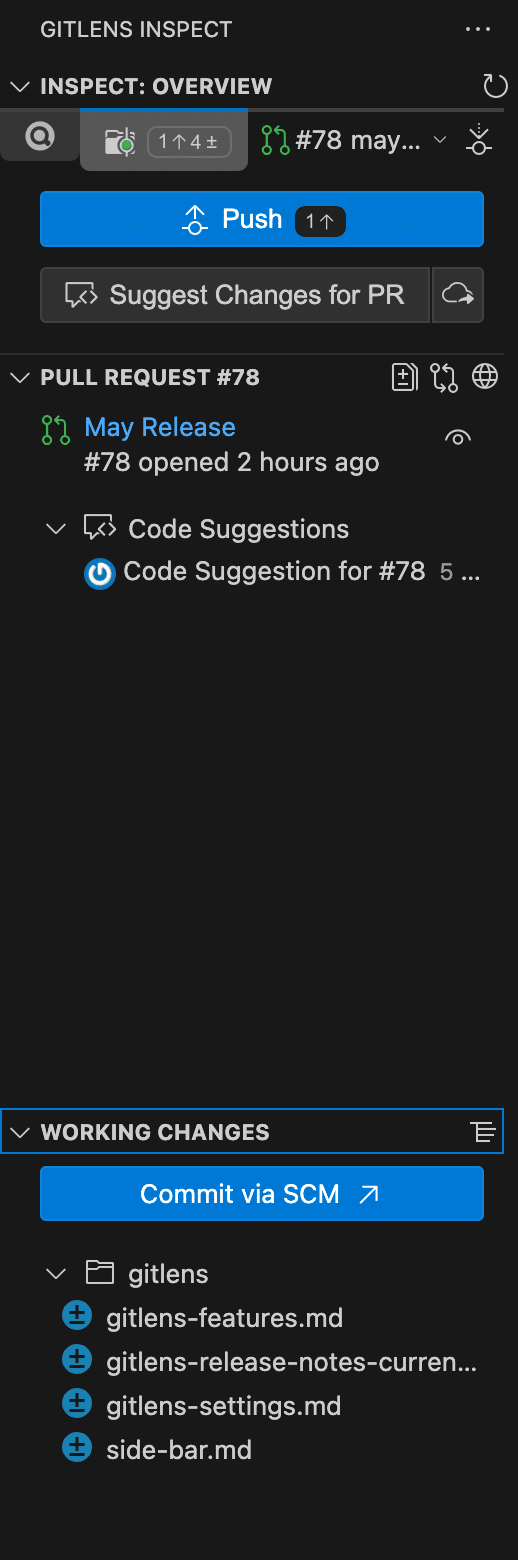
GitLens Inspect
The GitLens Inspect sidebar focuses on providing contextual insights related to the code you’re working on. It includes two tabs: Commit Details and Overview.
To open GitLens Inspect, launch the Command Palette (Cmd/Ctrl + Shift + P) and run:
GitLens: Show Inspect View
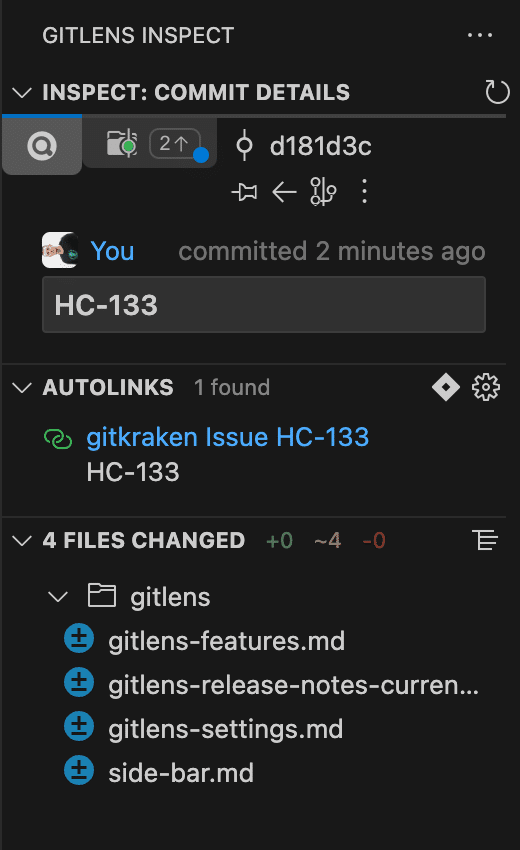
Commit Details
The Commit Details tab updates as you move your cursor through the file or select a commit in the Commit Graph. It shows information such as commit author, ID, modified files, and autolinks.
Overview
The Overview tab helps you stage or unstage changes, open files to view modifications, and access associated pull requests. You can also suggest changes or view Code Suggestions when working on a pull request.
Repositories View
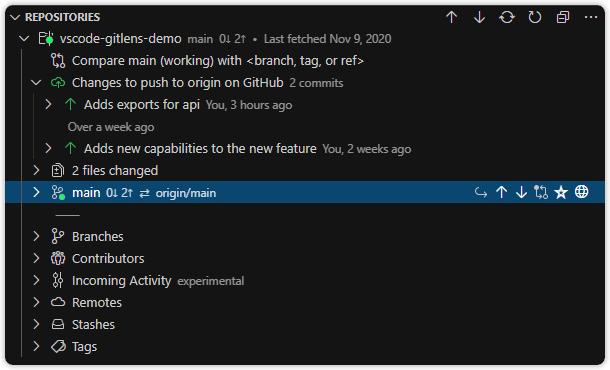
A hidden by default, customizable view to visualize, explore, and manage Git repositories.
The Repositories view lists all open Git repositories. It includes:
- A toggle to auto-refresh repository changes
- A toggle to switch file layout: list, tree, or auto
- Upstream status indicators:
- No dot — branch unpublished or no changes
- Green dot — commits ahead of upstream
- Red dot — commits behind upstream
- Yellow dot — ahead and behind
- A branch comparison tool — compare the current branch with a selected branch, tag, or ref:
- Behind — commits missing from current branch
- Ahead — commits present in current branch only
- Optionally show:
- Changed files in the working tree
- Current branch status with upstream (e.g., publish, up to date, changes to pull or push)
- Associated pull request
- Commit history (like the Commits view)
- Local branches (like the Branches view)
- Remotes and branches (like the Remotes view)
- Stashes, tags, and contributors
- Incoming Activity (experimental) — recent merge and pull events
File History View
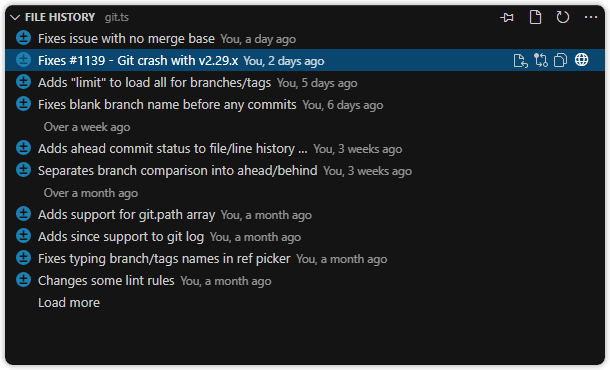
A customizable view to visualize, navigate, and explore the revision history of the current file or selected lines.
The File History view lists all commits that modified the current file on the active branch. It includes:
- A toggle to pin (pause) automatic tracking of the current editor
- A toggle to switch between file and line history
- The ability to change the base branch or reference for history
- (File history only) A toggle to follow renames
- (File history only) A toggle to show commits from all branches
- Merge conflict status (if applicable):
- Merge Changes — compare base and incoming changes to aid in resolving conflicts
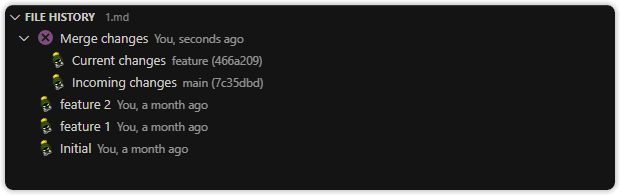
Line History View
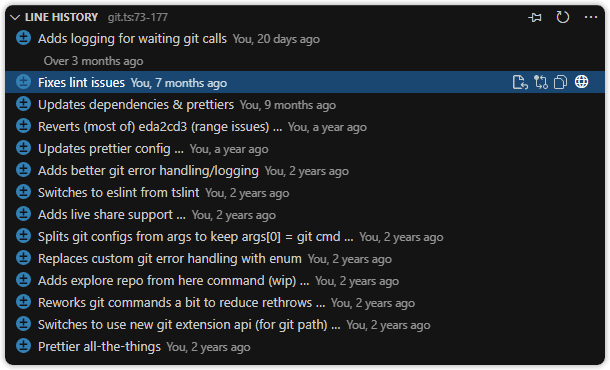
A hidden by default, customizable view to visualize, navigate, and explore the revision history of the selected lines of the current file.
The Line History view lists all commits that modified the selected lines. It provides:
- A toggle to pin (pause) automatic tracking of the current editor
- The ability to change the base branch or reference
- Merge conflict status (if applicable):
- Merge Changes — compare base and incoming changes to aid in resolving conflicts
Branches View
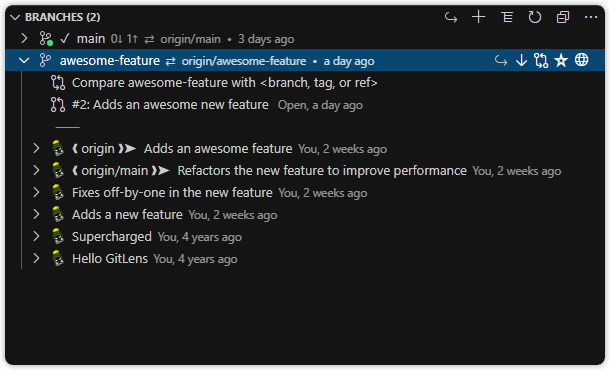
A customizable view to visualize, explore, and manage Git branches.
The Branches view lists all local branches and includes:
- A toggle to switch between list or tree layout
- A toggle to change file layout: list, tree, or auto
- Upstream status icons:
- No dot — branch unpublished or no changes
- Green dot — ahead of upstream
- Red dot — behind upstream
- Yellow dot — ahead and behind
- Status indicators:
✓— current branch▲(green) — unpushed changes▼(red) — unpulled changes▼▲(yellow) — diverged from upstream▲+(green) — unpublished branch!(dark red) — missing upstream branch
- A comparison tool — compare a branch with another branch, tag, or ref:
- Behind — commits missing from the branch
- Ahead — commits present on the branch only
- Number of files changed — across all comparison points
- Branch status:
- Publish — shown for unpublished branches
- Changes to push — unpublished commits
- Changes to pull — incoming commits
- Associated pull request — shown when linked to a branch
Remotes View
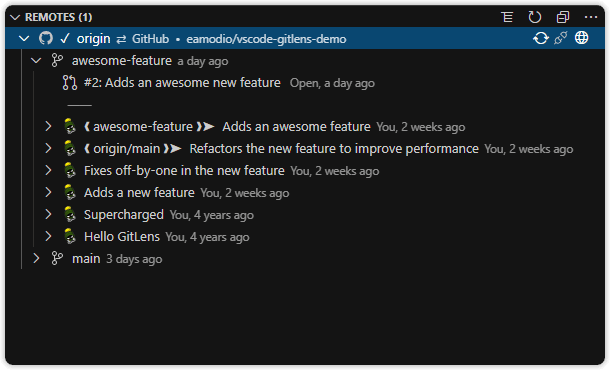
A customizable view to visualize, explore, and manage Git remotes and remote branches.
The Remotes view lists all remotes and their remote branches. It includes:
- A toggle to switch between list or tree layout for branches
- A toggle to change file layout: list, tree, or auto
- A toggle to connect to supported remote providers for enhanced integration with pull requests, issues, avatars, and more
Stashes View
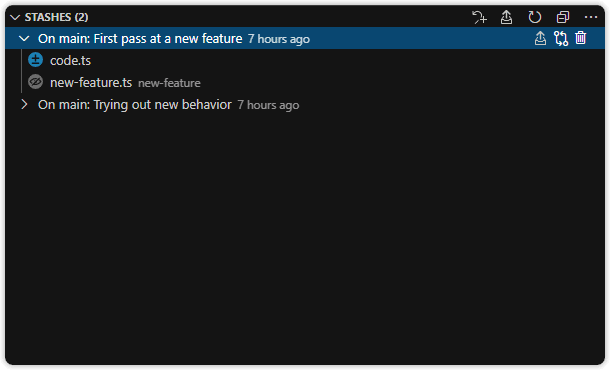
A customizable view to visualize, explore, and manage Git stashes.
The Stashes view lists all stashes and includes:
- A toggle to change file layout: list, tree, or auto
Tags View
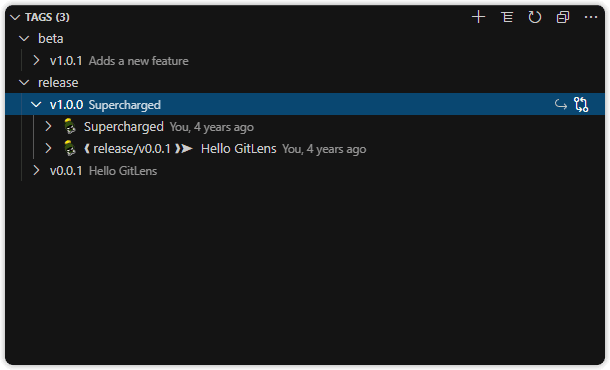
A customizable view to visualize, explore, and manage Git tags.
The Tags view lists all tags and includes:
- A toggle to switch tag layout: list or tree
- A toggle to change file layout: list, tree, or auto
Launchpad View PRO
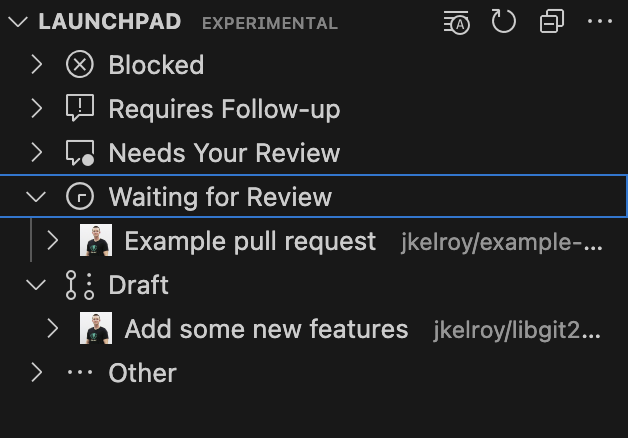
The Launchpad view provides an always-visible panel for pull request activity. You can view pull request details in a tree format and take action directly from the sidebar.
To enable this experimental feature, either run the Show Launchpad View command or set gitlens.views.launchpad.enabled to true in your settings file.
Workspaces
Workspaces offer a convenient way to group and manage multiple repositories for easy access. Whether working solo or as part of a team, Workspaces help streamline your development process. You can include local repositories or GitKraken Workspaces—cloud-hosted repositories or those managed through GitKraken services.
To access Workspaces, open the GitLens Home menu and find them in the lower-left panel. Alternatively, search “Workspaces” via the Command Palette.
Note: Using cloud Workspaces requires a GitKraken account. Sharing cloud Workspaces requires a trial or paid subscription.
Creating a Workspace
Click the + icon next to GitKraken Workspaces to create a new Workspace. Enter a name and description, and optionally connect a provider.
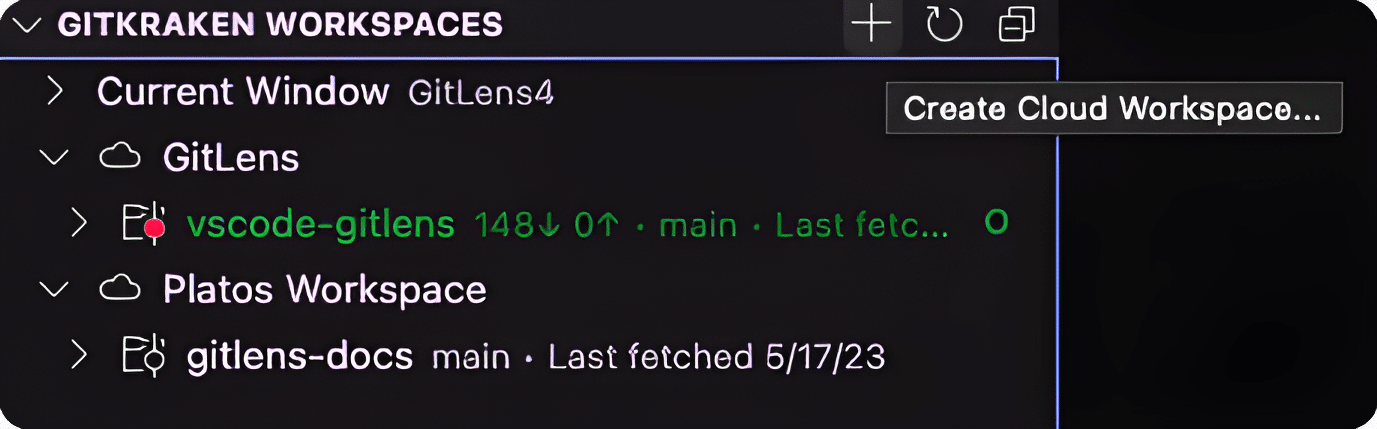
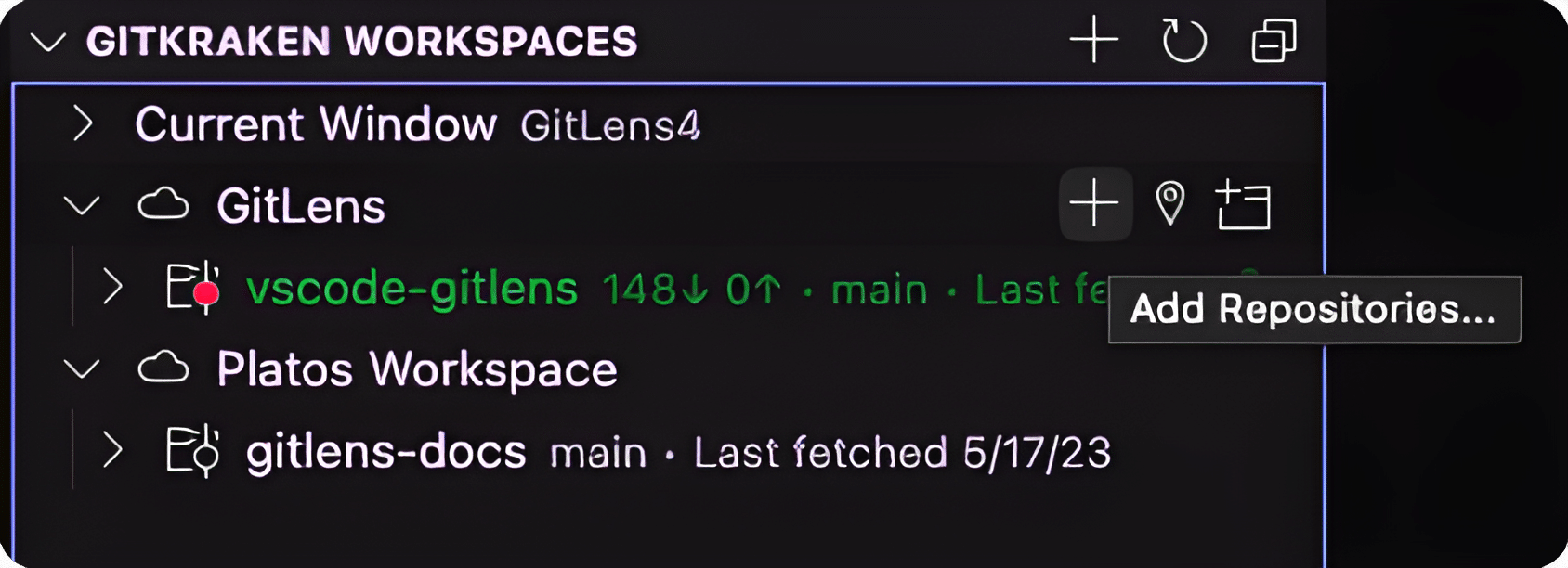
Adding Repositories
Add repositories to your Workspace using the + icon under the Workspace tab. Click the Refresh icon to sync updates.
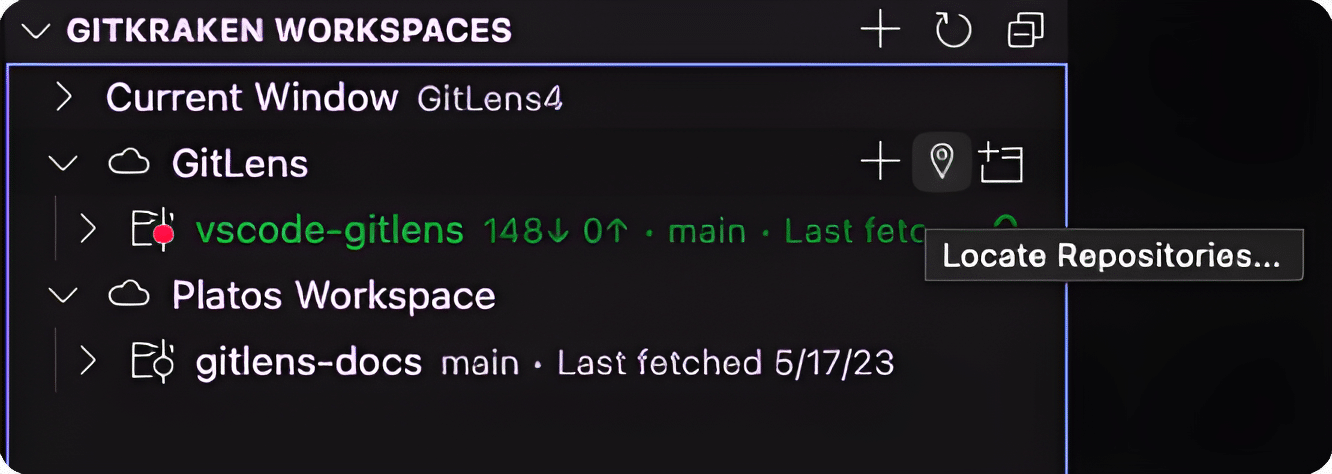
Locating Repositories
To find a repository’s location on disk, click the Locate Repositories (pin icon). Select a parent folder, and GitLens will scan it for repositories.
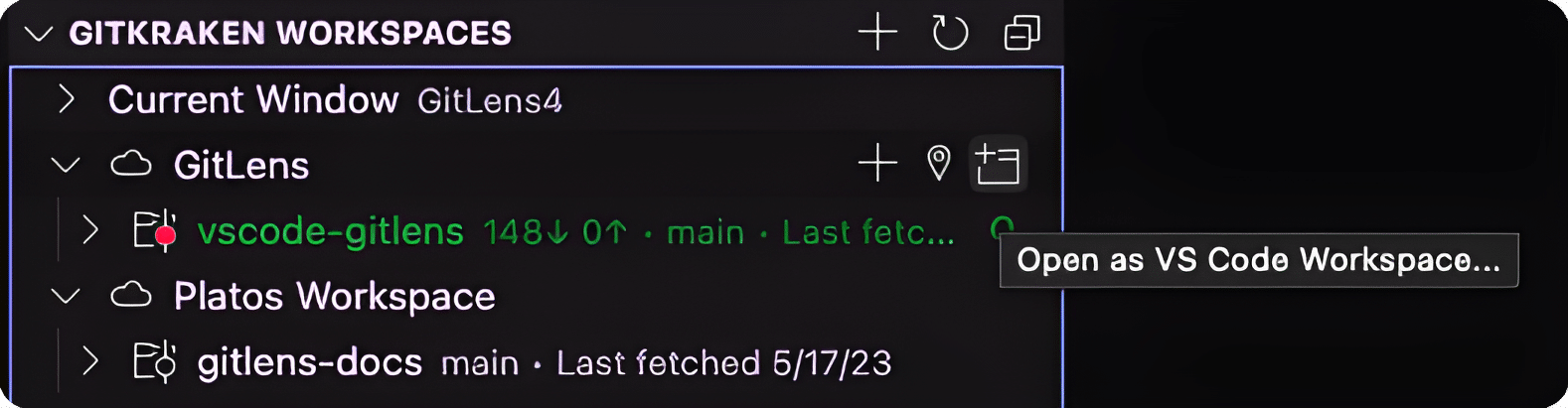
Opening Repositories
To open a repository, click the Open Repository in New Window icon.
Pro Tip: Hold Alt/Option while clicking to open in the current window.
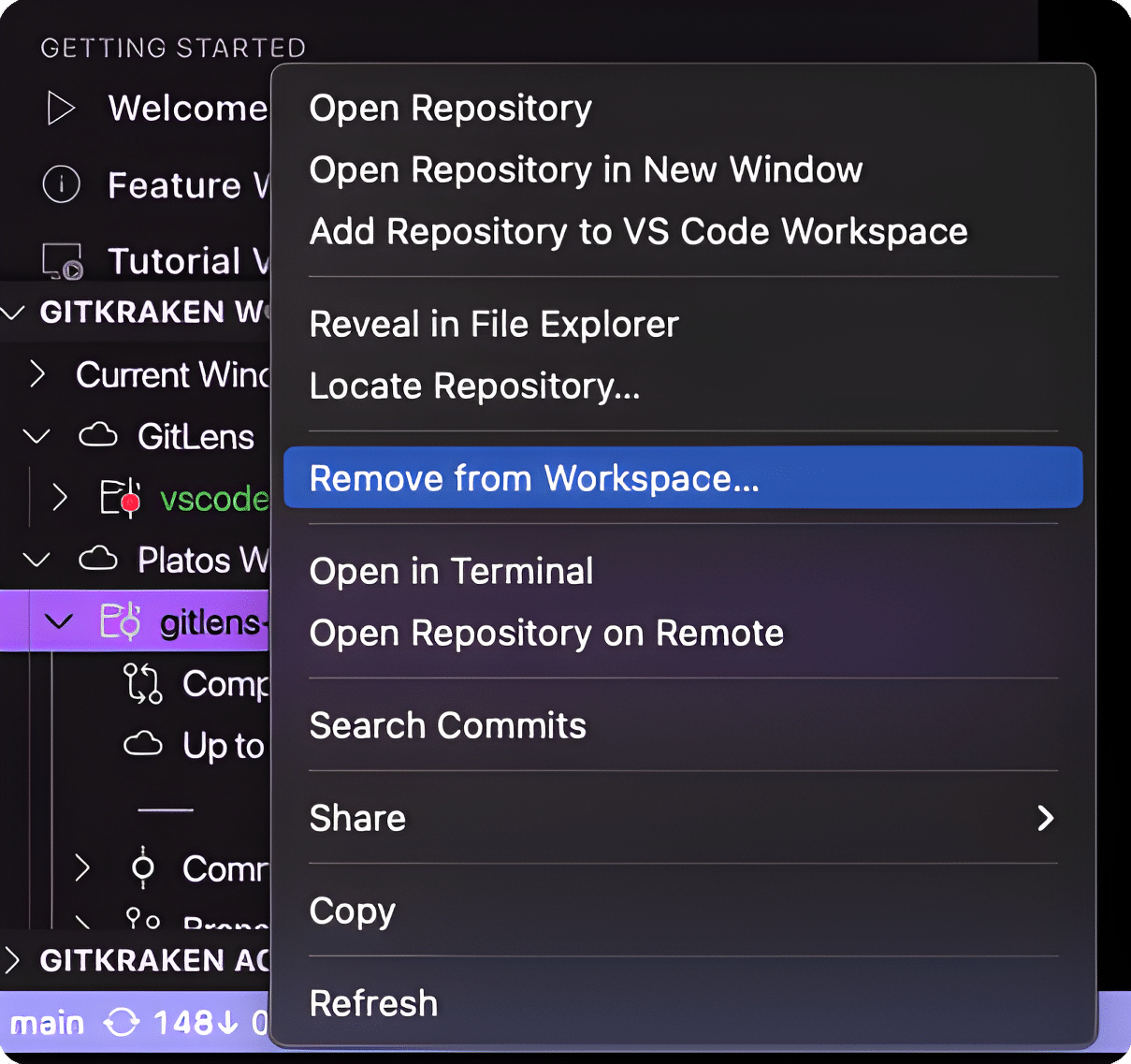
Removing Repositories
Right-click a repository and choose Remove repository from Workspace to remove it.
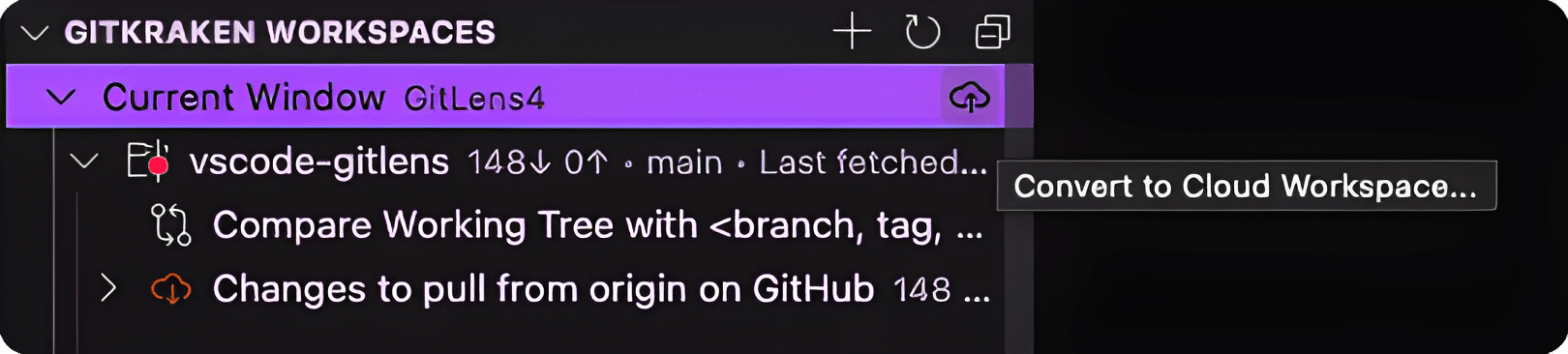
Converting to Cloud Workspaces
To convert a local Workspace, click Convert to Cloud Workspace, add a name and description, and save. Your Workspace will be available across GitKraken tools.
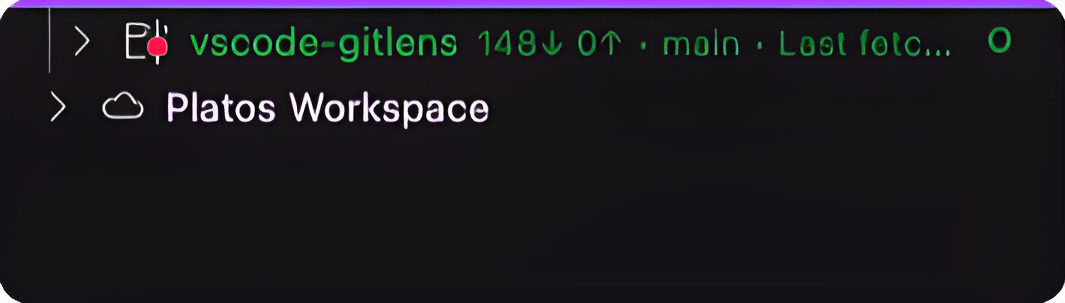
Workspace Indicators and Colors
Workspace status indicators use symbols and colors, such as a green O for the currently open Workspace.
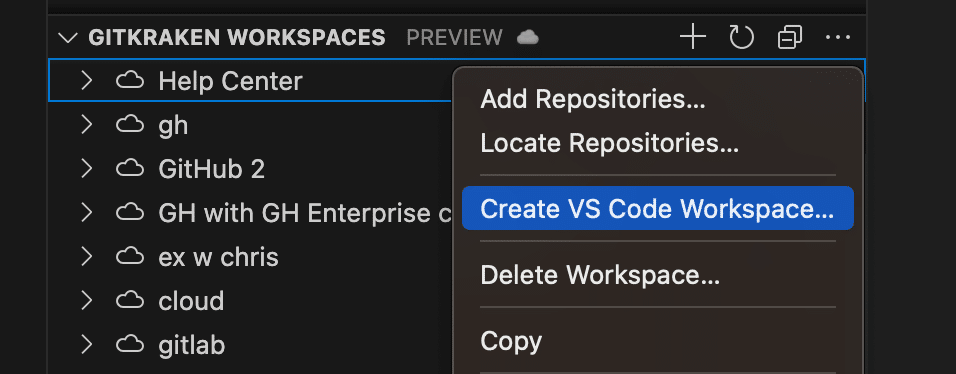
Workspace Linking
You can link a GitKraken Workspace to a VS Code workspace.
Linked VS Code workspaces can be opened from their cloud counterpart using Open VS Code Workspace in New Window (hold Alt to open in the current window).
When you add repositories to a GitKraken Workspace, they can be auto-added to its linked VS Code workspace. You choose the auto-add behavior when creating the workspace and can modify it later via the Change Linked Workspace Auto-Add Behavior command.
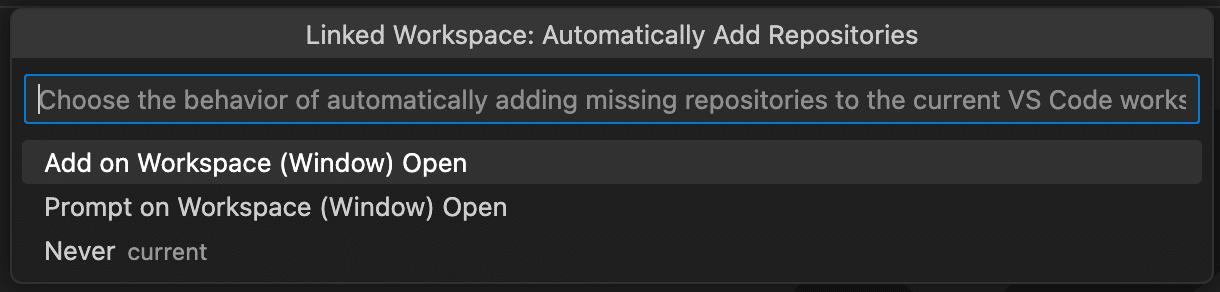
To manually add repositories, use the Add Repositories from Linked Workspace command.
Worktrees View
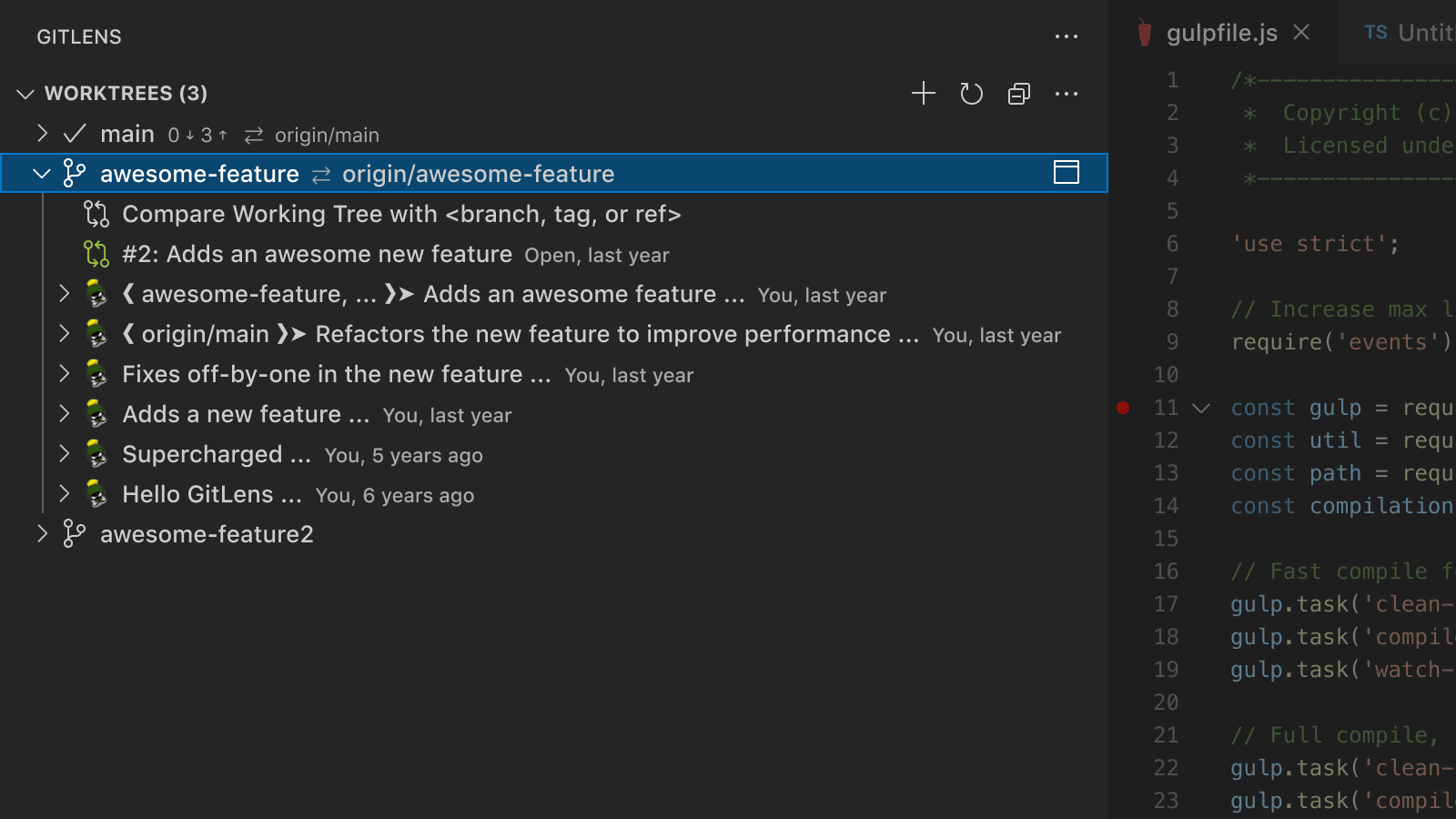
A customizable view to create, view, and manage Git worktrees. Worktrees allow you to check out multiple branches at once within the same repository—useful for parallel development or testing workflows without switching branches.
Contributors View
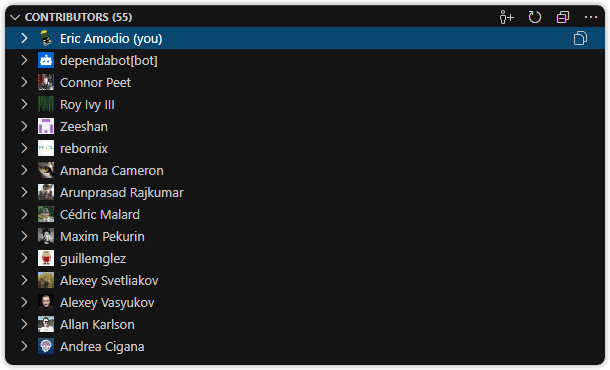
A hidden by default, customizable view to explore repository contributors.
The Contributors view lists all contributors and includes:
- A toggle to change file layout: list, tree, or auto
Search & Compare View
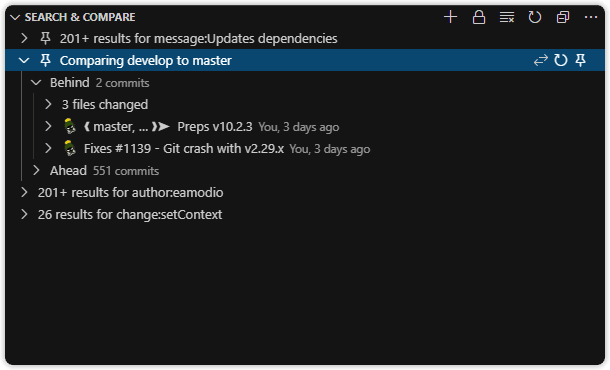
A hidden by default, customizable view to search commit history or compare branches, tags, commits, and more.
The Search & Compare view displays pinnable results from search or comparison operations. It includes:
- A toggle to retain previous results
- A toggle to change file layout: list, tree, or auto
Pinnable Search
Search commits by message, author, file, ID, or patch using:
- Search Commits (
gitlens.showCommitSearch):<message>— message match@<pattern>— author match#<sha>— commit SHA:<path/glob>— filename pattern~<pattern>— patch content match
- Show File History (
gitlens.showQuickFileHistory) - Show Commit (
gitlens.showQuickCommitDetails)
Pinnable Comparison
Compare any two references:
- Behind — commits missing from the target branch
- Ahead — commits unique to the target branch
- Number of files changed — file diffs between the two references
Comparison commands include:
gitlens.views.compareWithUpstreamgitlens.views.compareWithWorkinggitlens.views.compareWithHeadgitlens.views.compareWithSelectedgitlens.views.compareAncestryWithWorking
You can use checkboxes next to files to track review progress.