Last updated: January 2026
Push, pull, and fetch operations are essential for synchronizing local work with remote repositories in GitKraken Desktop.
Add a Remote
To add a remote:
- Hover over
Remote in the Left Panel.
- Click the icon.
- Enter the remote URL or choose from integration-based dropdowns (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket).
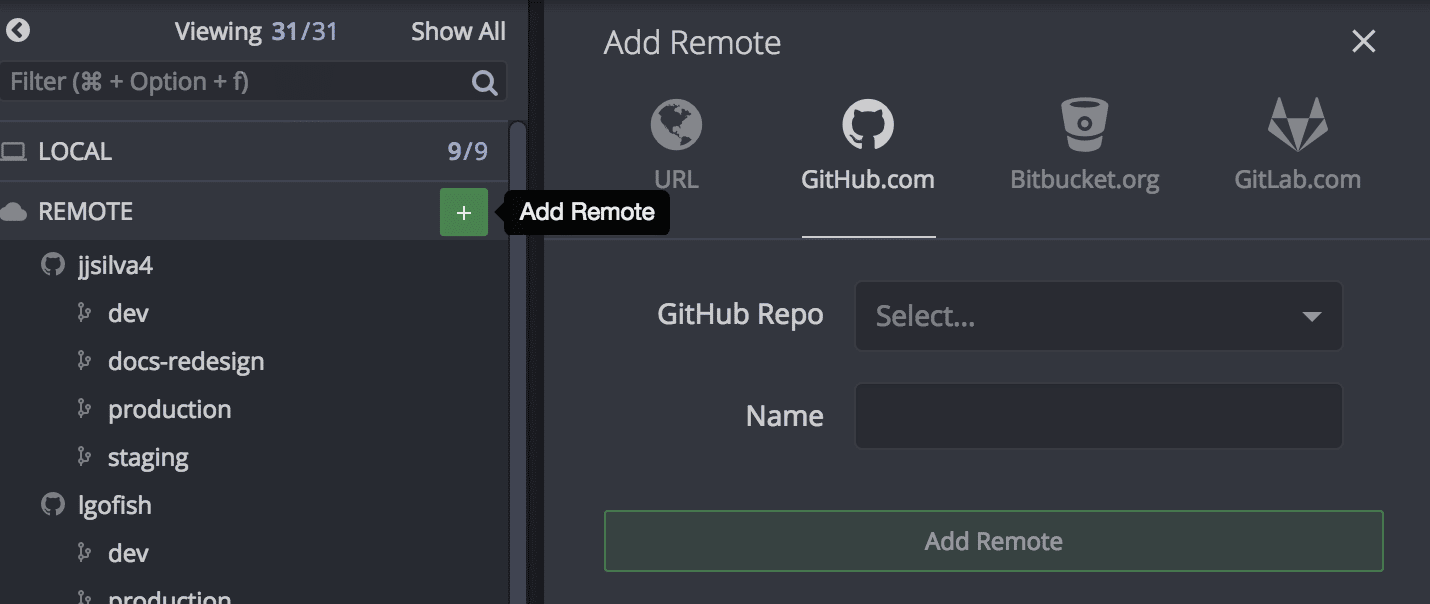
Note: Integration dropdowns show forks only. For non-fork remotes, use the URL option.
Remote icons in the Commit Graph:
- GitHub
- Bitbucket
- GitLab
- Azure DevOps
- Other
Push Changes 
To push local commits to a remote branch:
- Click Push in the main toolbar
- Or right-click a branch and select Push

If a remote branch doesn’t exist yet, GitKraken will prompt you to name and create it.
Caution: If fast-forwarding fails, GitKraken may offer a Force Push option. Use with care.
Drag and Drop Push
Drag a branch onto a remote branch (in the graph or Left Panel) to trigger a push.
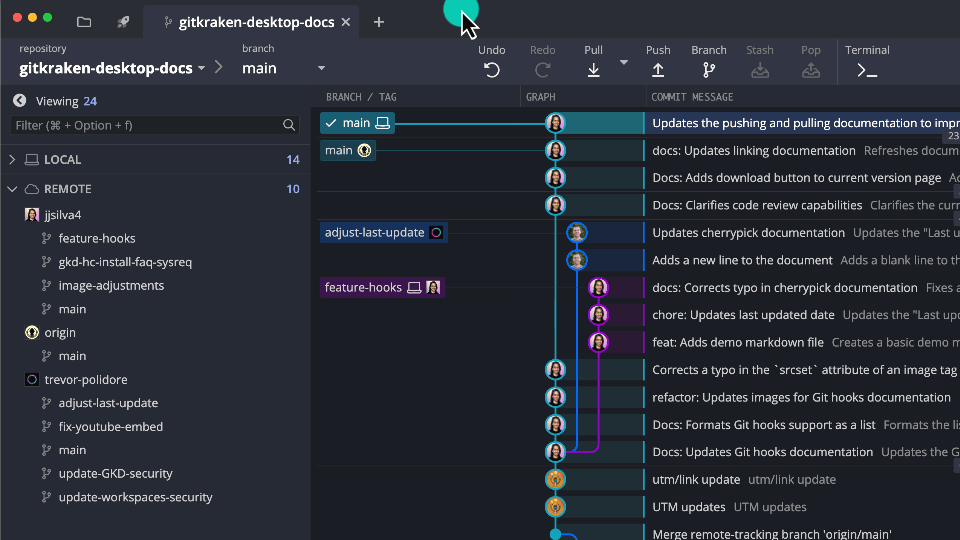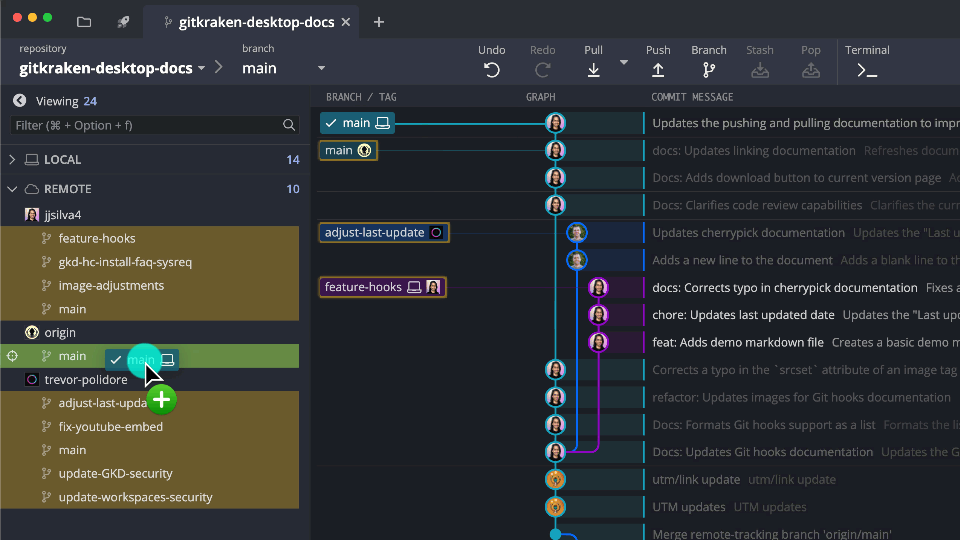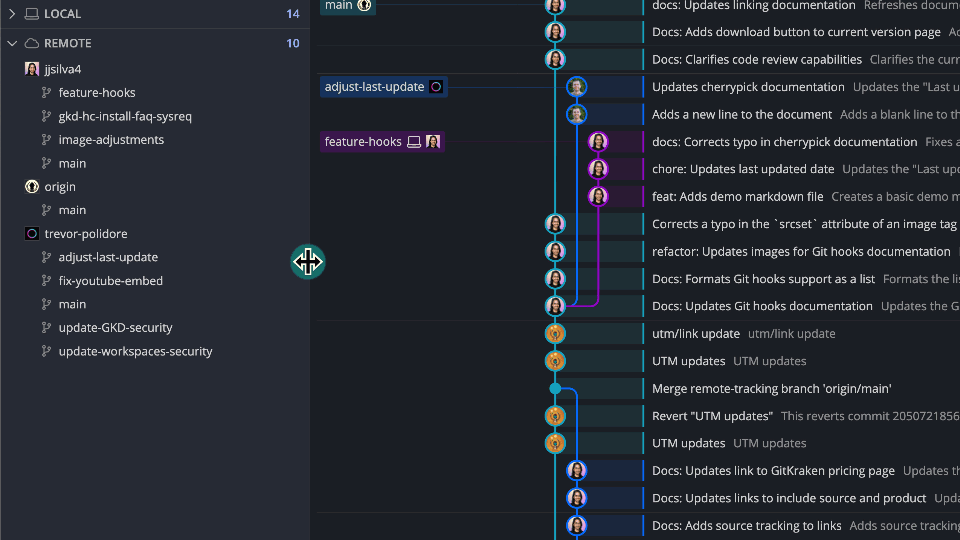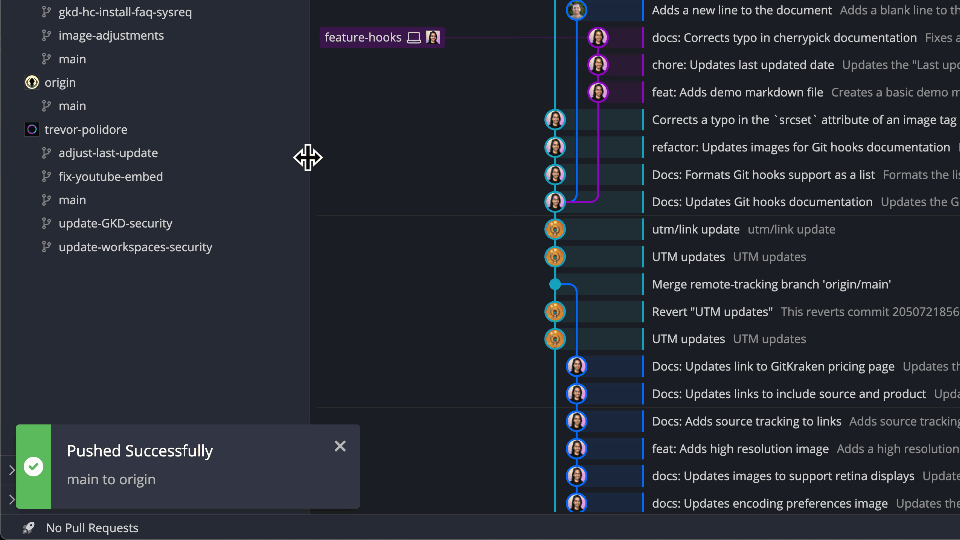
Fetch
Fetching retrieves updates from remotes but doesn’t change your working directory.
Fetch All
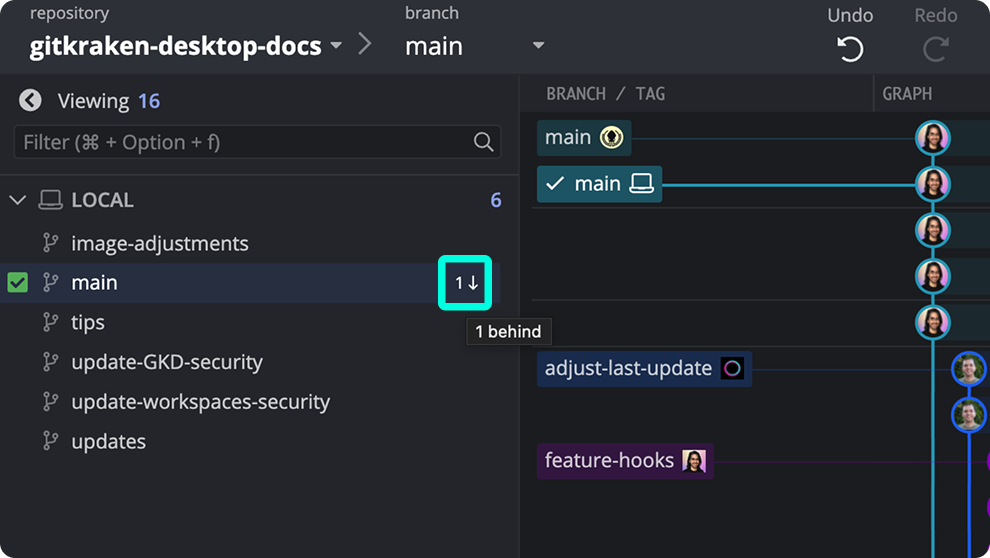
Shows how far ahead/behind your branches are compared to the remote.
Fetching runs automatically every minute. Adjust the interval in Preferences > General.
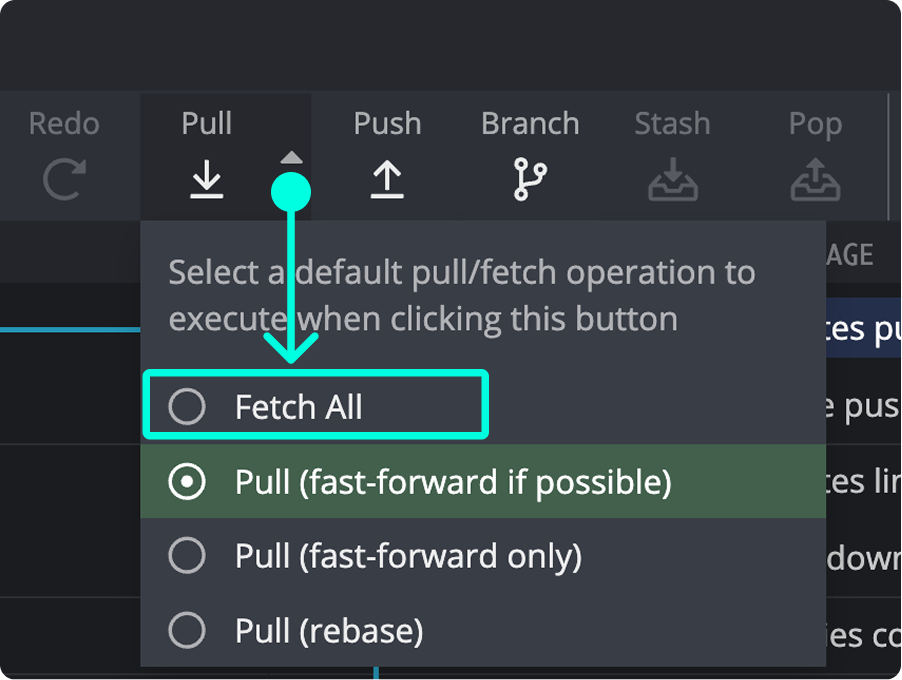
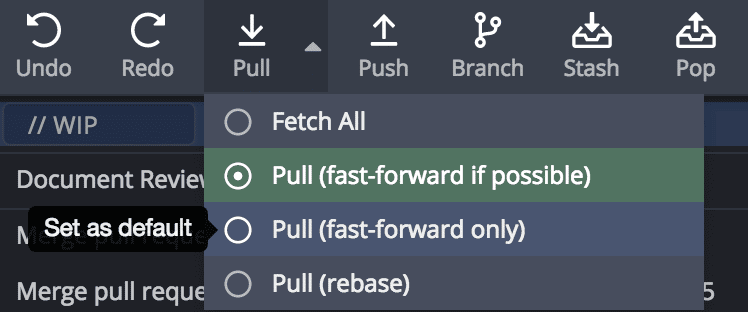
Pull Options 
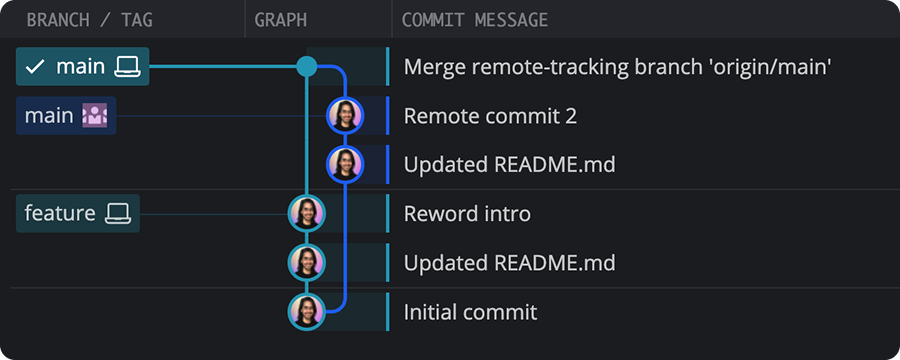
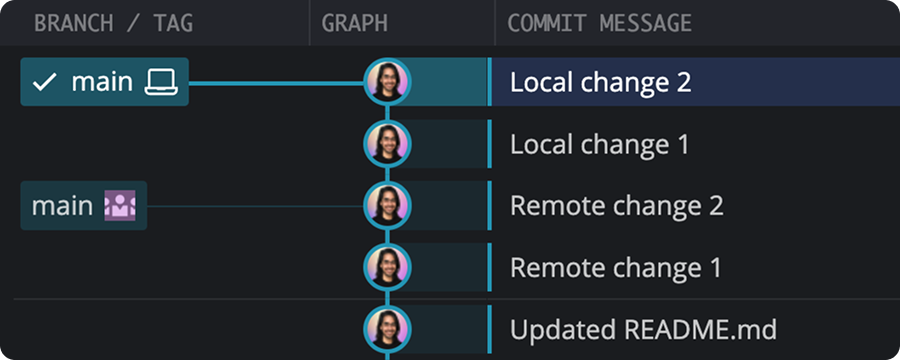
Pulling performs a fetch and then updates your local branch.
Pull (fast-forward if possible)
Fast-forwards your branch if there are no conflicting commits; otherwise, merges.
Pull (fast-forward only)
Attempts to fast-forward. If not possible, no action is taken.
Pull (rebase)
Temporarily stashes your commits, pulls from remote, and replays your changes on top.
Set Pull Behavior
Select a default pull method via the dropdown menu.
Set Upstream Branch
The upstream defines the remote branch a local branch tracks.
- Right-click a branch to set its upstream
- Or click the button
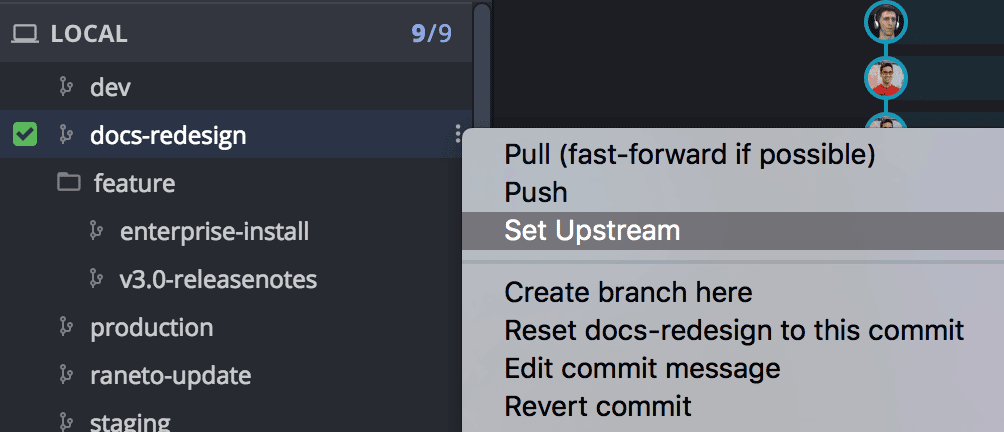
You can also drag and drop to push instead of explicitly setting the upstream: