What’s on this page:
- How is git data indexed?
- Automatic indexing
- Manual indexing
- Indexing definitions
- Branch and pull/merge request name index triggers
The Git Integration for Jira Cloud app automatically indexes commits, branches, tags, and pull/merge requests. Previously, the system updated all repositories and integrations on a strict schedule – approximately every 8 minutes after the last indexing process finished for an account. This worked for small accounts and provided consistency but was inefficient for large accounts with repositories that rarely change.
Starting on October 28, 2019, the system calculates indexing based on per-repository activity. The overall goals are to reduce the strain on git services and make the indexing service more available for webhook triggers.
The system only indexes pull/merge requests for repositories connected using the Full feature integrations panel in Manage Git Repositories. You can access them via the Jira Developer Panel on the right sidebar of a Jira issue. Git repositories added individually via SSH or HTTPS credentials do not show pull/merge requests.
How is git data indexed?
Git Integration for Jira Cloud indexes a variety of Git and Git-related data once a Jira administrator connects it. The table below describes how the system accesses each data type. All data remains stored until a Jira administrator removes the integration or the subscription is cancelled or expires.
See our Privacy Policy and Data Deletion Policy.
| Data Type | Method |
|---|---|
| Commits | Git clone |
| Branches | Git clone |
| Tags | Git clone |
| Pull requests | API |
| Merge requests | API |
| List of repositories | API |
Automatic indexing
Indexing repositories
An internal process runs approximately every 8 minutes to review repositories eligible for change checking. The system checks all repositories for changes at least once daily. A repository change (commit, branch, tag) causes the system to calculate the Next repository check as: a quarter of the time since the last repository update was detected.
For example, if the last commit was detected 4 hours ago, the system schedules the Next repository check in 1 hour.
The system recalculates Next repository check times on each indexer check.
Indexing integrations
An internal process runs approximately every 8 minutes to review integrations eligible for change checking. The system checks integrations (for example, GitLab, GitHub, etc) during each Next indexer check via the git service’s API for available repositories.
The system checks all repositories for changes at least once daily. A repository change (commit, branch, tag) causes the system to calculate the Next repository check as: a quarter of the time since the last repository update was detected.
For example, if the last commit was detected 4 hours ago, the system schedules the Next repository check in 1 hour.
The system recalculates Next repository check times on each indexer check.
Triggering automatic reindexes via webhooks
Automatic indexing records changes in a timely manner for all types of repositories, but ideally, changes should be indexed immediately. Configure webhooks to trigger automatic reindexing for immediate reindex times.
When the indexing service receives webhooks, it reduces automatic indexing to once hourly.
For more information on configuring webhooks, see: Indexing triggers.
Automatic indexing period limits
The table below describes the automatic indexing period limits:
| Action | Conditions | Min. period | Max. period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Check a repository | No webhook (PR or push) arrives for the repository | 450 secs | 24 hr |
| Check a repository | Webhooks (PR or push) arrives for the repository | 1 hr | 24 hr |
| Check an integration | Regardless of arriving webhooks | 19.2 hrs | 24 hr |
Manual indexing
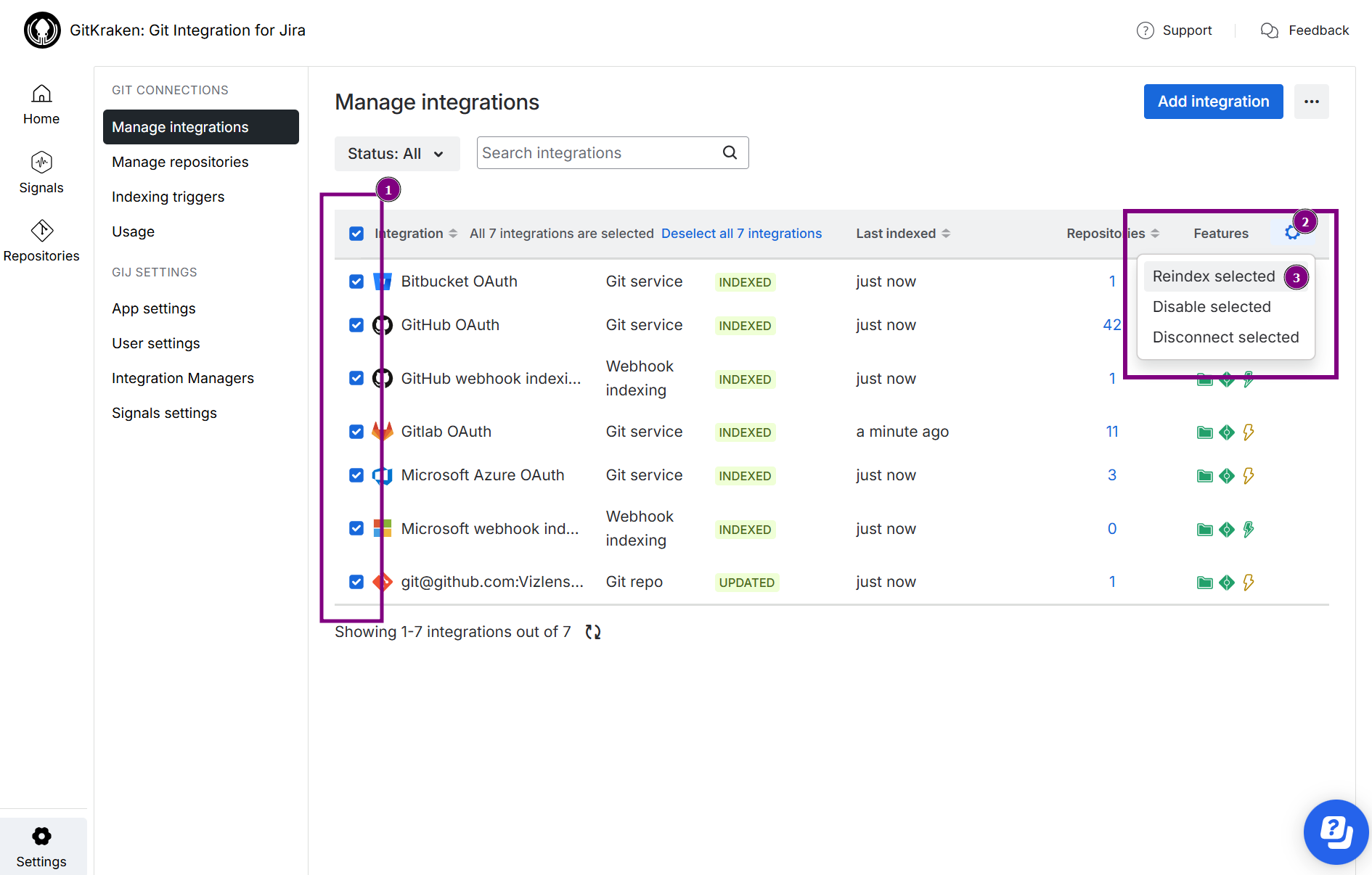
Reindex all
You can update all repositories and integrations manually via the Manage Git repositories screen by selecting the Reindex All button:
Repositories
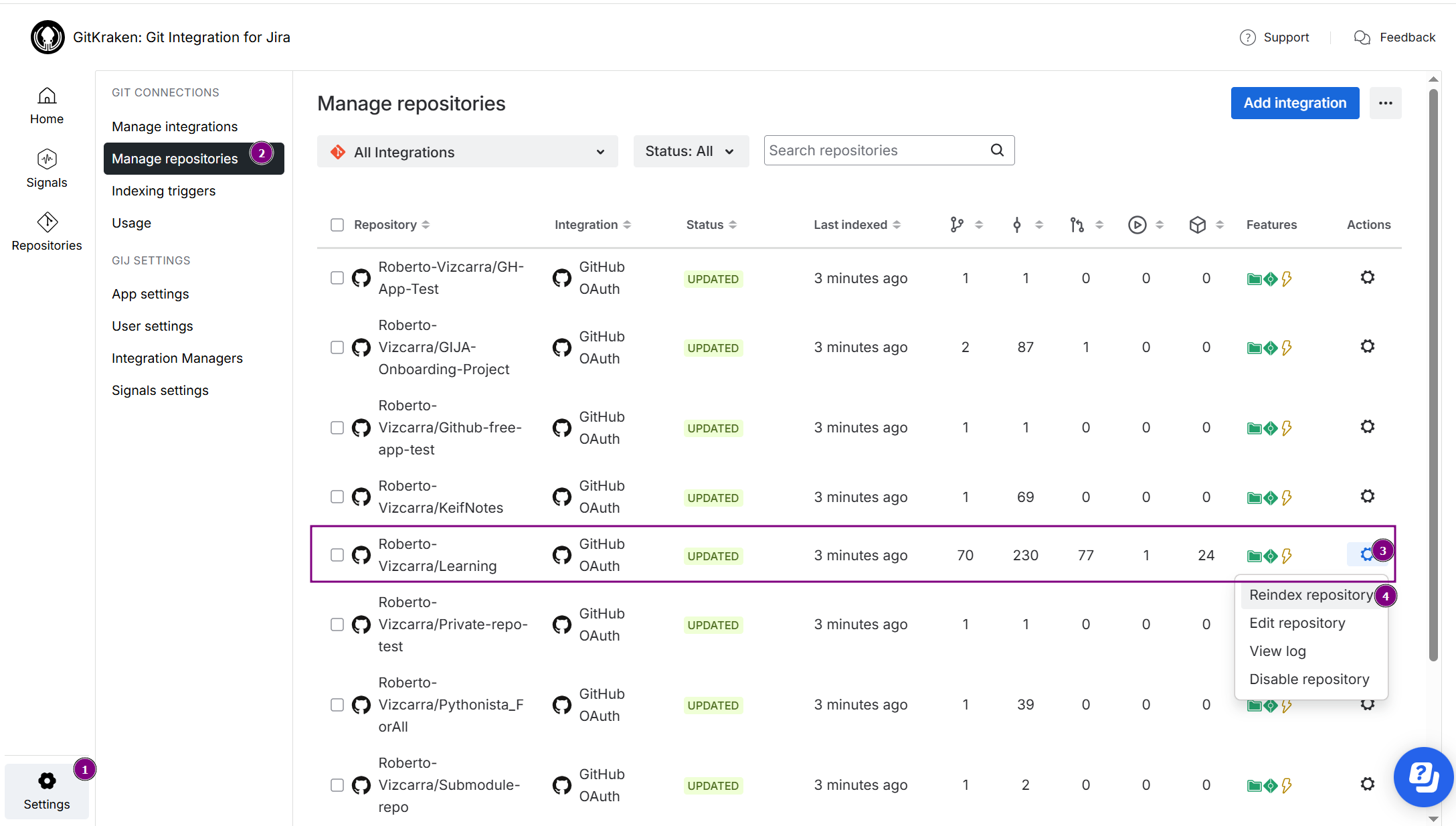
You can update repositories manually via the Manage git repositories screen by opening the ![]() Actions menu and selecting Reindex repository:
Actions menu and selecting Reindex repository:
Integrations
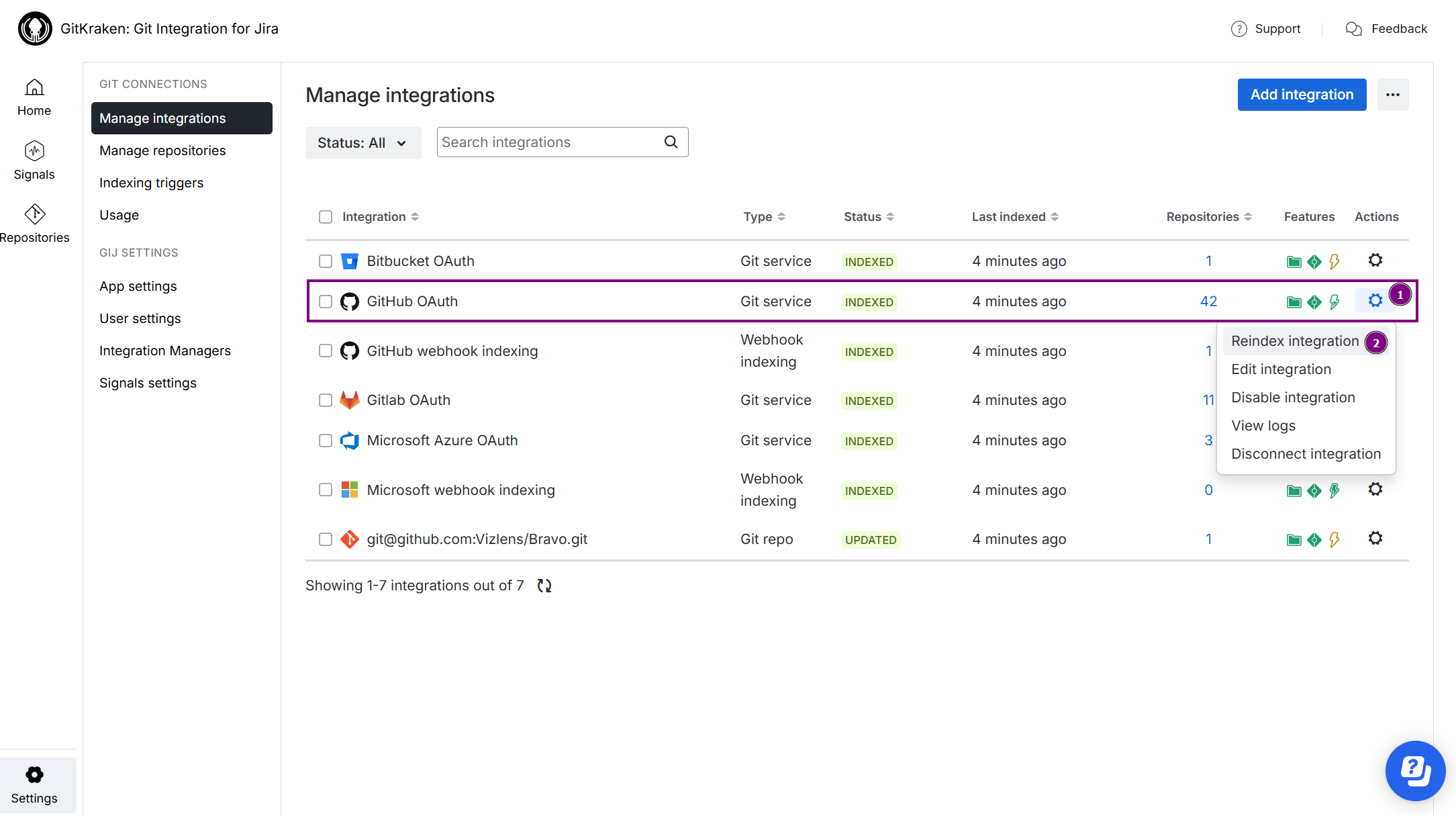
You can update integrations manually via the Manage git repositories screen by opening the ![]() Actions menu and selecting Reindex integration:
Actions menu and selecting Reindex integration:
Indexing statuses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| INDEXED | The integration or repository has been indexed and no errors were detected. |
| QUEUED | The integration or repository is actively queued for indexing. |
| INDEXING | The indexer is actively checking the integration or repository for changes. |
| ERROR | The integration has at least one repository in an error state (and not updating) and at least one repository was successfully updated. |
| ERROR | The integration or all repositories are in an error state and are not updating. |
Indexing errors
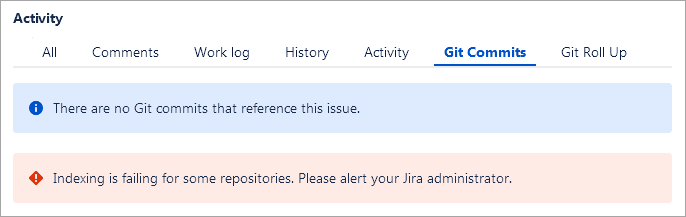
A notification about indexing errors appears in the Git Commits tab so Jira administrators receive immediate alerts.
Branch and pull/merge request name index triggers
Pull/merge requests are still indexed based on branch name even if the PR/MR title does not have the Jira issue key – as long as the branch name contains the Jira issue key.
Last updated: December 2025