Last updated: June 2025
GitKraken’s remote hosting platform integrations may require users to have a certificate in place. Follow the instructions below to add a certificate to your local certificate store.
Adding a Self-Signed Certificate
Self-signed certificates must be added to your trusted root directory before GitKraken will recognize the cert. This can be done through your operating system or in many browsers.
Note: If you have the Git Executable enabled, SSL settings in the global .gitconfig file are honored by GitKraken Desktop for actions performed by the Git executable.
Using Google Chrome on Windows
An easy way to install a certificate so that GitKraken can use it is via Google Chrome.
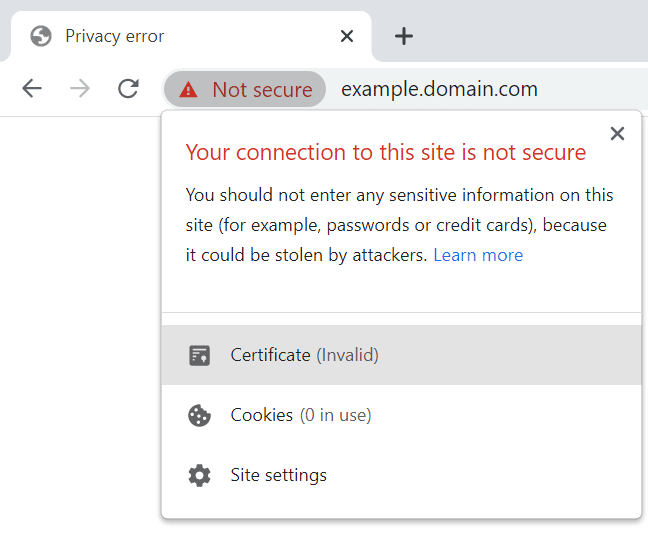
To generate a self-signed certificate, navigate to your remote hosting service’s website. You should see something like this:
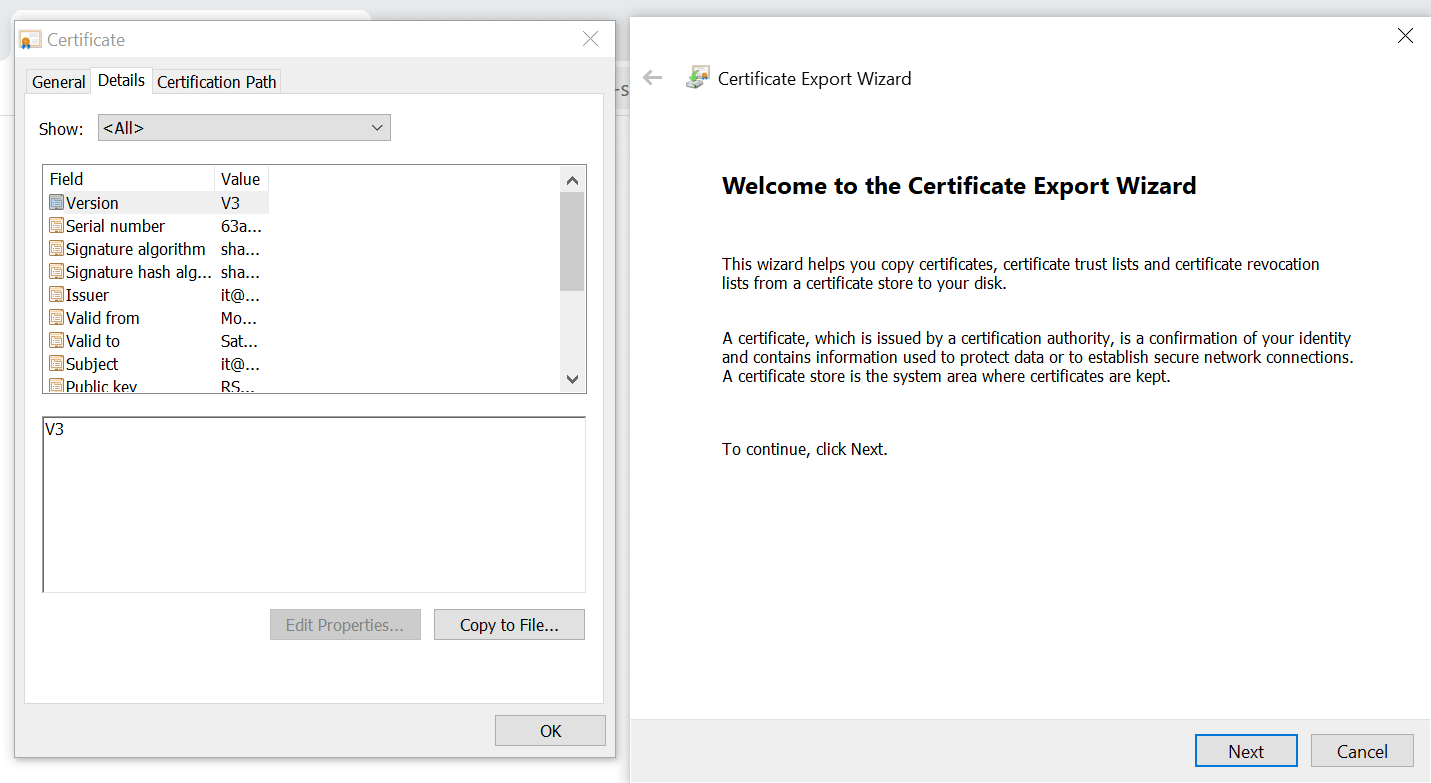
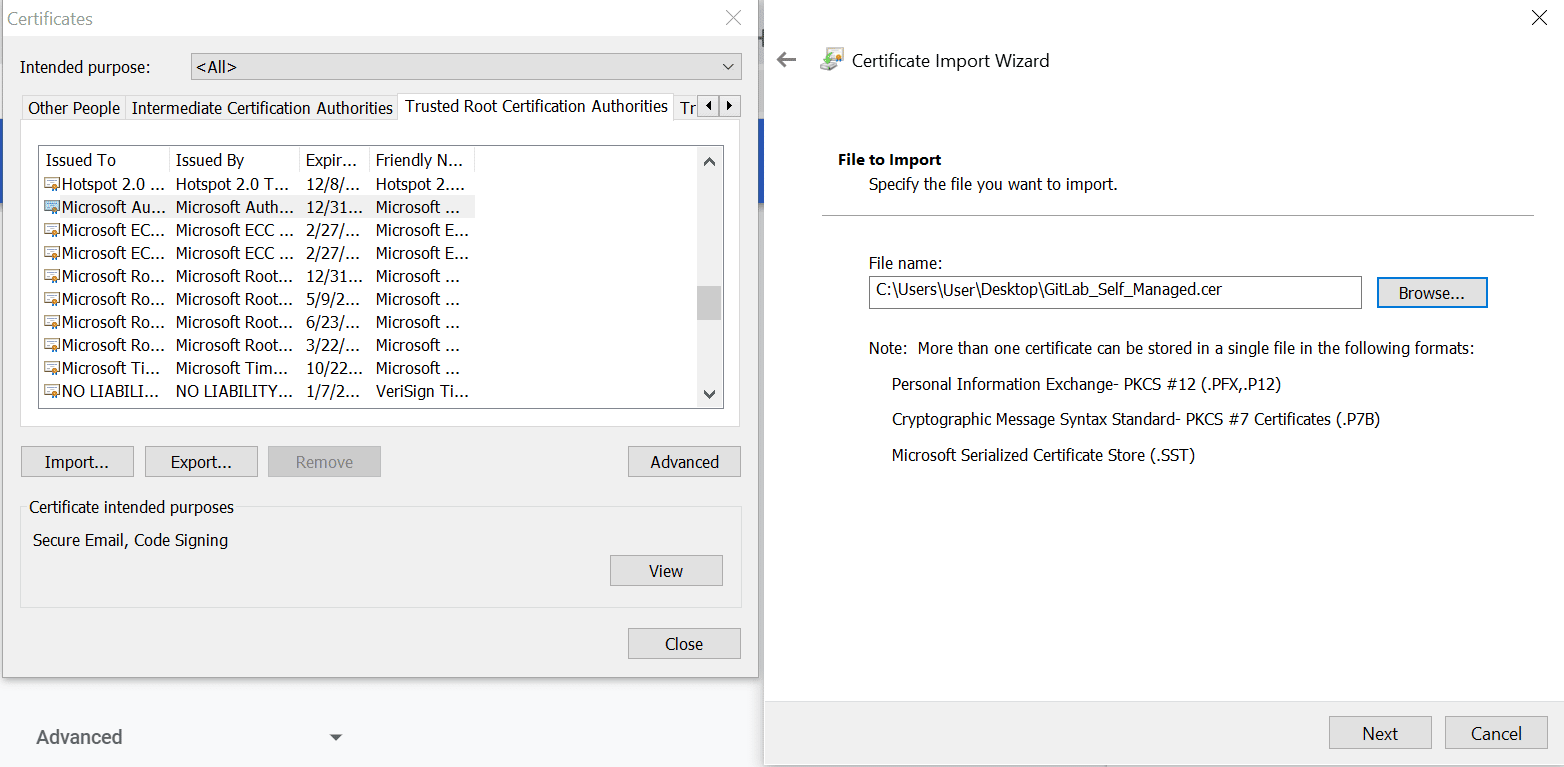
Click on the certificate, go to Details, click Copy to File..., and follow the Certificate Export Wizard.
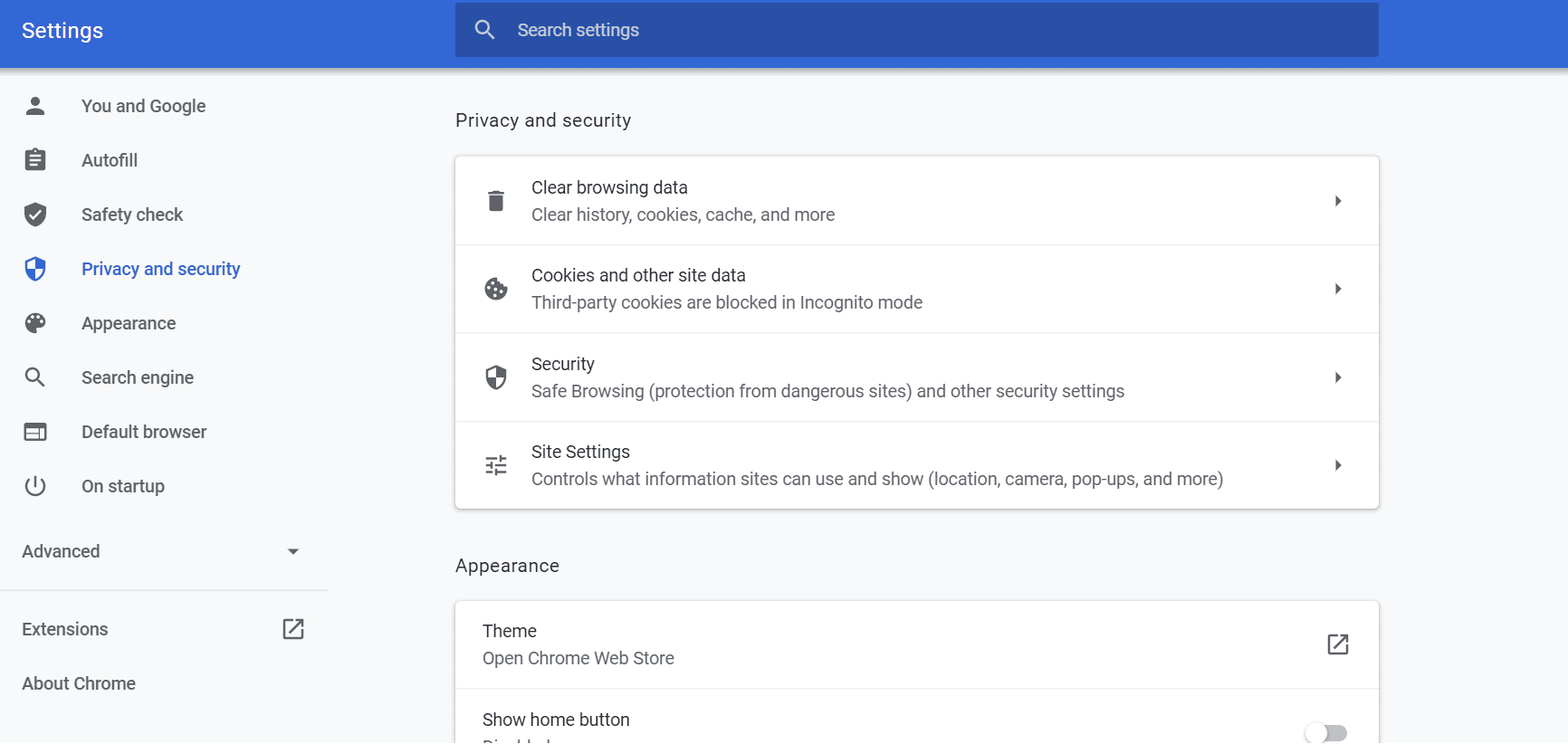
Open Chrome’s Settings menu from the top-right .

Navigate to Privacy & Security Security:
Scroll down and click Manage certificates. Use the wizard to import the certificate.
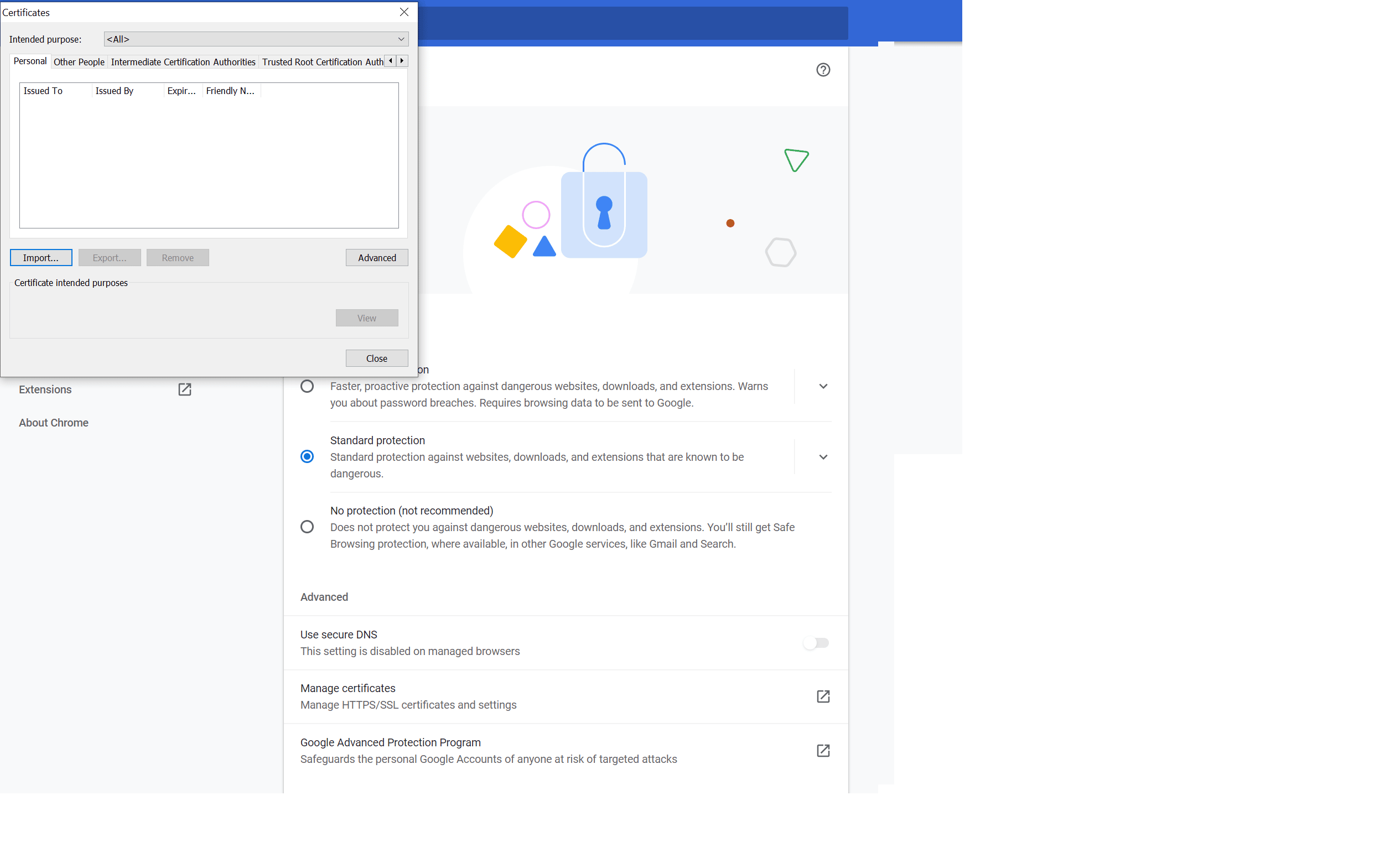
Ensure that the certificate is added to your trusted root certificates.
Using Safari on Mac
Open Safari and navigate to your remote hosting service.
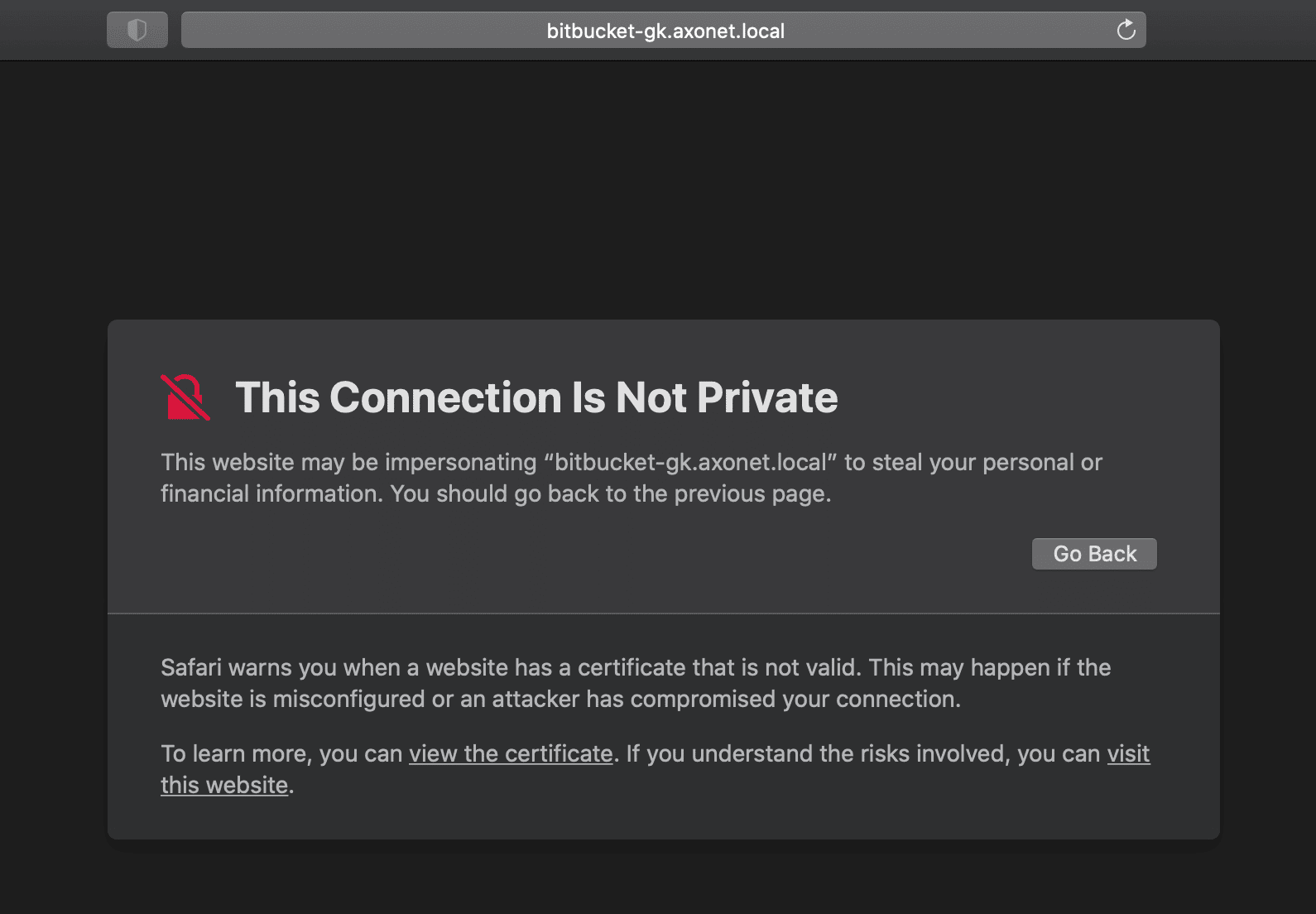
Click to open the certificate window:
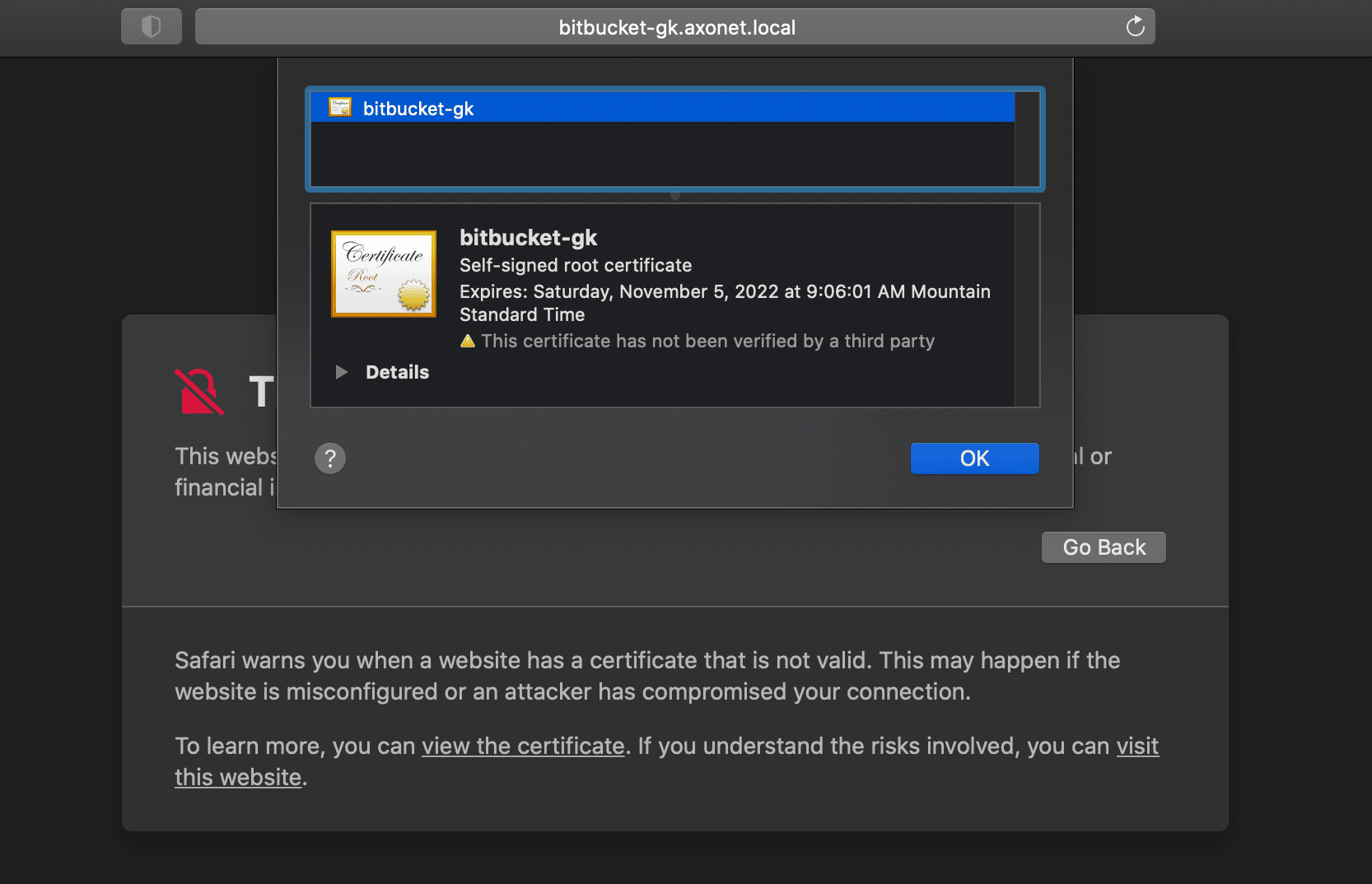
Hold down the Option key and drag the certificate icon to the desktop. This saves it as a .pem file.
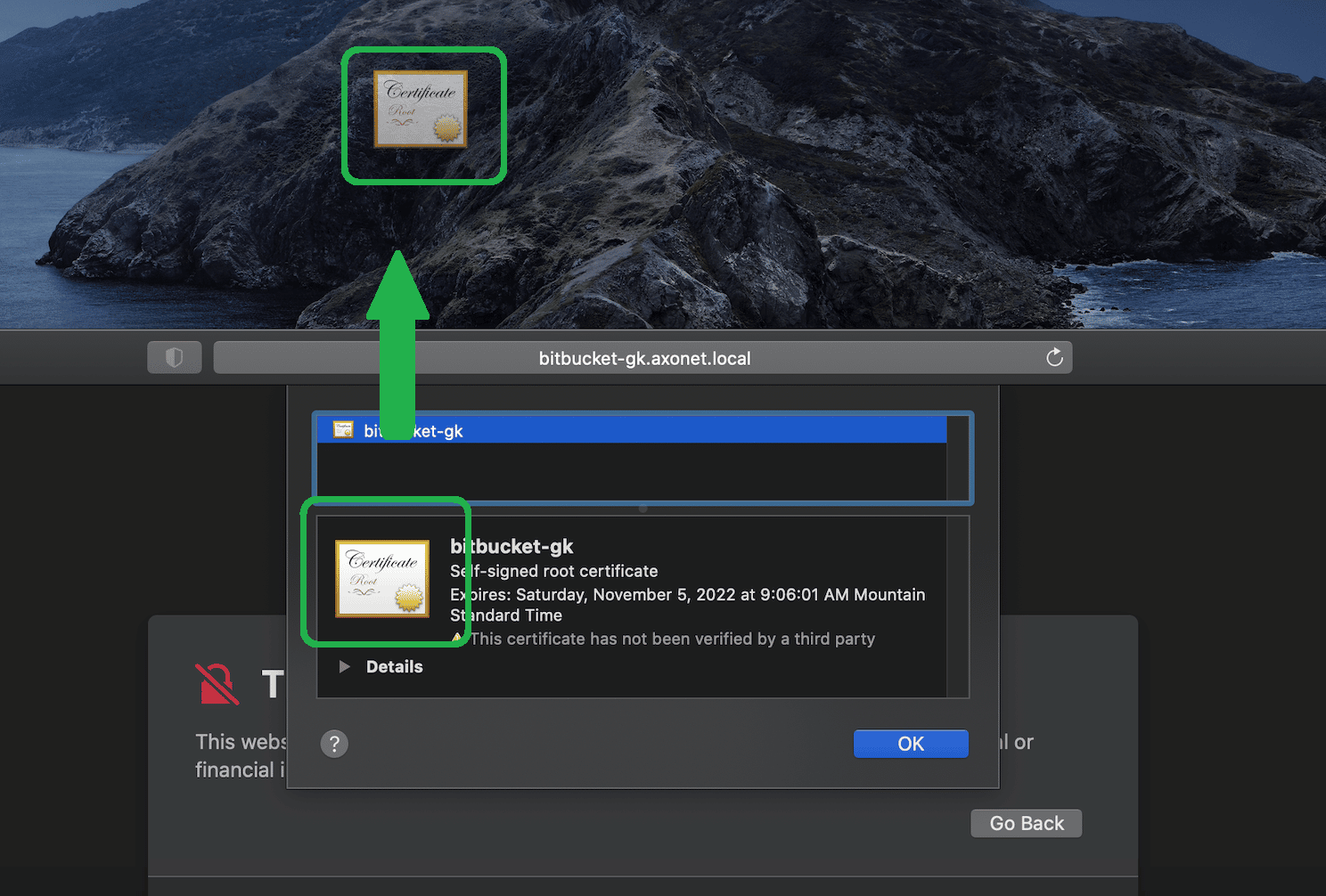
Double-click the file to open your macOS Keychain.
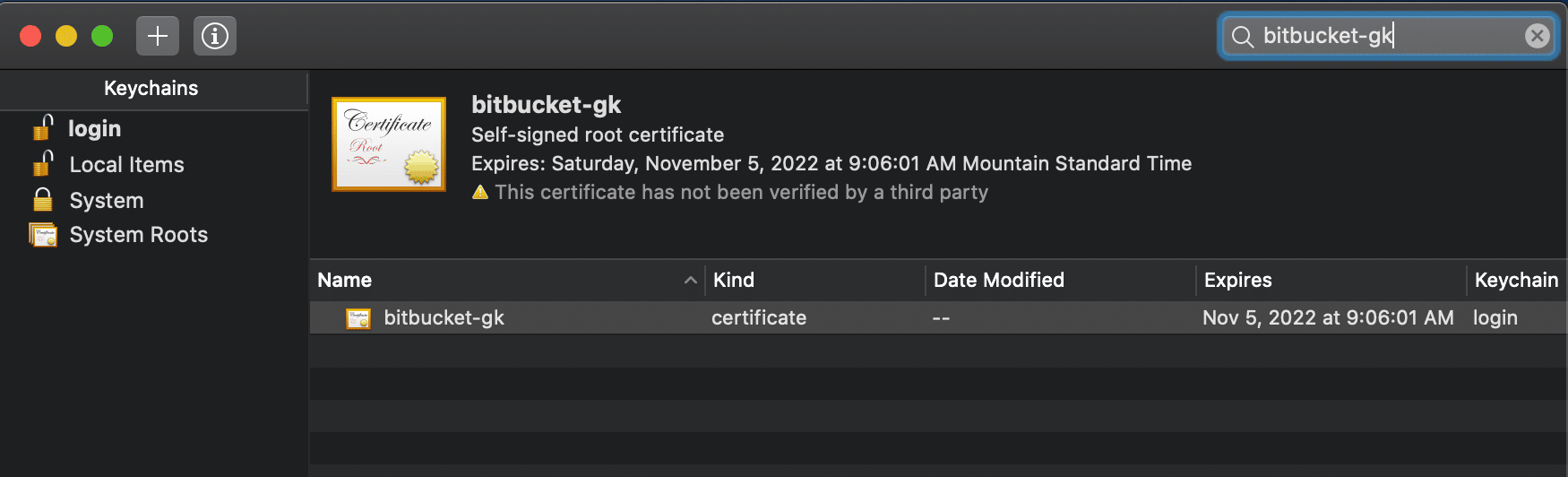
Locate the certificate in the login section and double-click to configure.
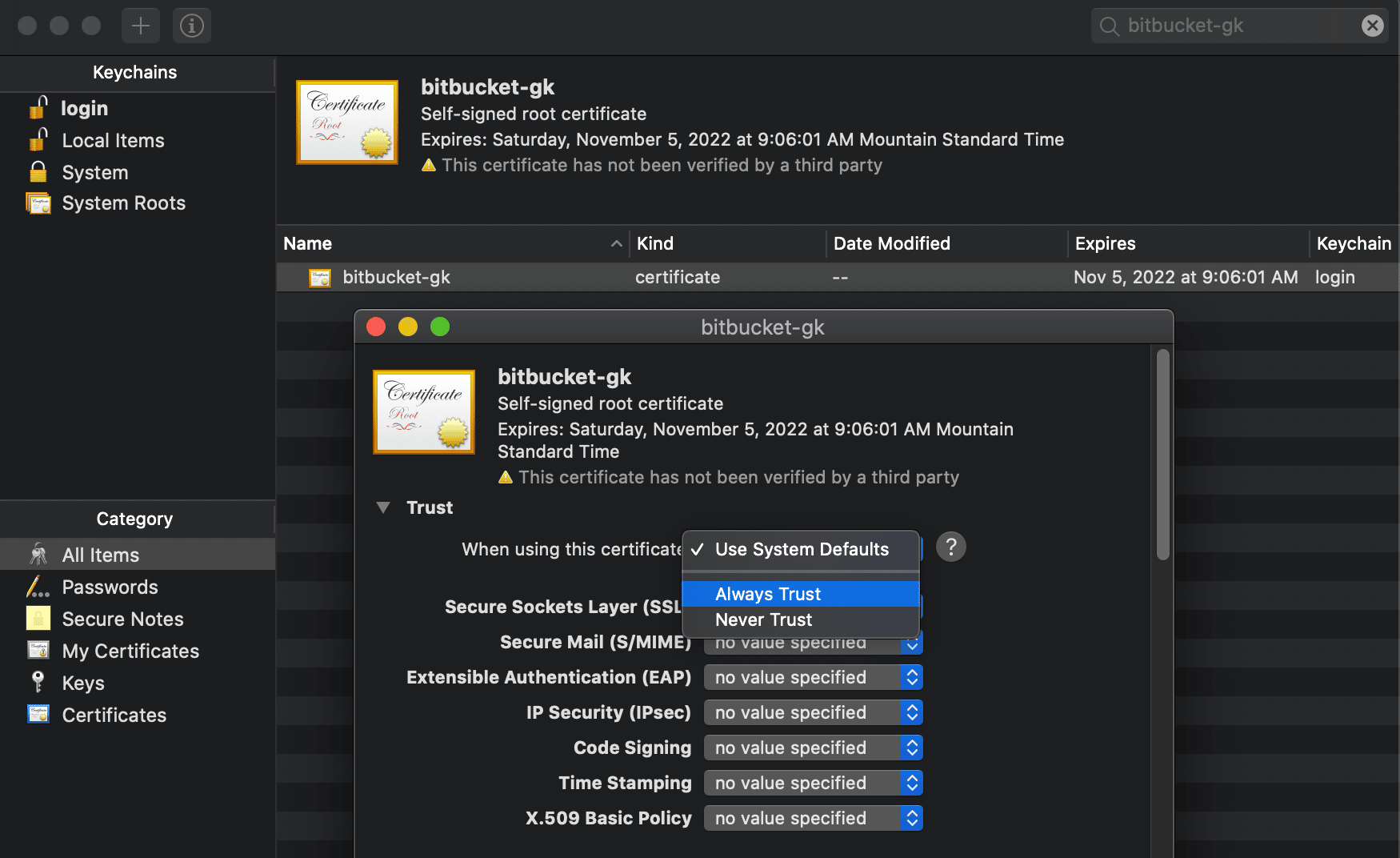
Set the trust level to Always Trust. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Using Chrome on Ubuntu Linux
Follow the same certificate export steps described in the Windows section. Then:
- Open a terminal and go to your Downloads folder.
- Run the following commands:
openssl x509 -outform der -in DOWNLOADED-CERT-NAME -out DOWNLOADED-CERT-NAME.crtcertutil -d sql:$HOME/.pki/nssdb -A -t "CT,C,C" -n DOWNLOADED-CERT-NAME.crt -i DOWNLOADED-CERT-NAME.crt- Verify the certificate:
certutil -d sql:$HOME/.pki/nssdb -LClose and reopen Chrome to confirm the certificate warning no longer appears.
Common Certificate Errors
Error: Invalid SSL Certificate
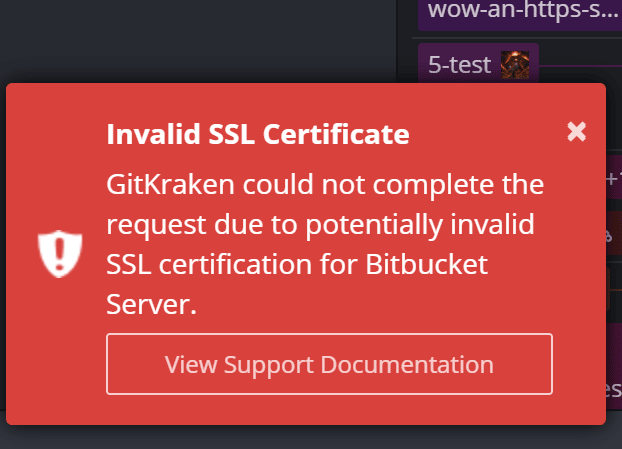
This usually indicates the certificate is invalid or missing. Add a certificate to your local store.
Additional Details
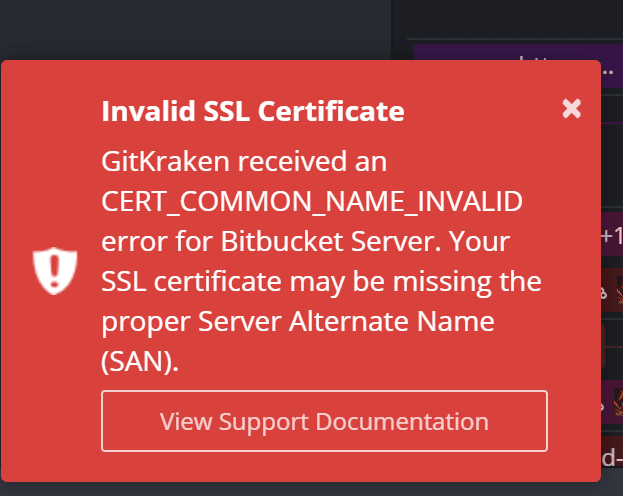
These errors often point to issues like a missing Server Alternate Name (SAN). Contact your server administrator to fix and reissue the certificate.
Operating System Guides
Use the links below for more help installing certificates by OS:
| Windows | Microsoft Docs |
| OSX | Apple Docs |
| Linux | Ubuntu Docs |