Integrate Azure DevOps Server/TFS with Jira Cloud
Quickly learn how to connect Azure DevOps Server/TFS git repositories via Git Integration for Jira app.
The Git Integration for Jira app supports Azure Repos.
What’s on this page:
- Integrate Azure DevOps Server/TFS with Jira Cloud
- Creating personal access tokens
- Permissions
- Using Git service integration and OAuth
- Single git repository integration
- Troubleshooting integration
- Webhooks and web linking
- Linking Azure DevOps Server/TFS git commits to Jira Cloud
- Viewing git commits in Jira Cloud
- Working with branches and pull requests with Azure DevOps Server/TFS
- Default branch
- Creating branches
- Creating pull requests
- Merging branch to master
- More Integration Guides
Creating personal access tokens
If you have not yet generated a personal access token (PAT), you can create one by following the simple steps in this article – use the table of content anchor link to go to the Azure DevOps Server/TFS section.
Permissions
Set Azure DevOps Server/TFS repository permissions according to your organization’s rules. Viewing commits from Jira requires the user to have at least Read or View permissions. For branch/pull request creation, set specific service users with Write permissions.
Using Git service integration and OAuth
This process requires an existing Microsoft account with Azure DevOps Server/TFS git projects.
We recommend using the Git service integrations panel to connect multiple repositories from your Azure DevOps Server/TFS account.
-
On your Jira side bar, go to Apps ➜ Git Integration for Jira, then Settings ➜ Manage Integrations
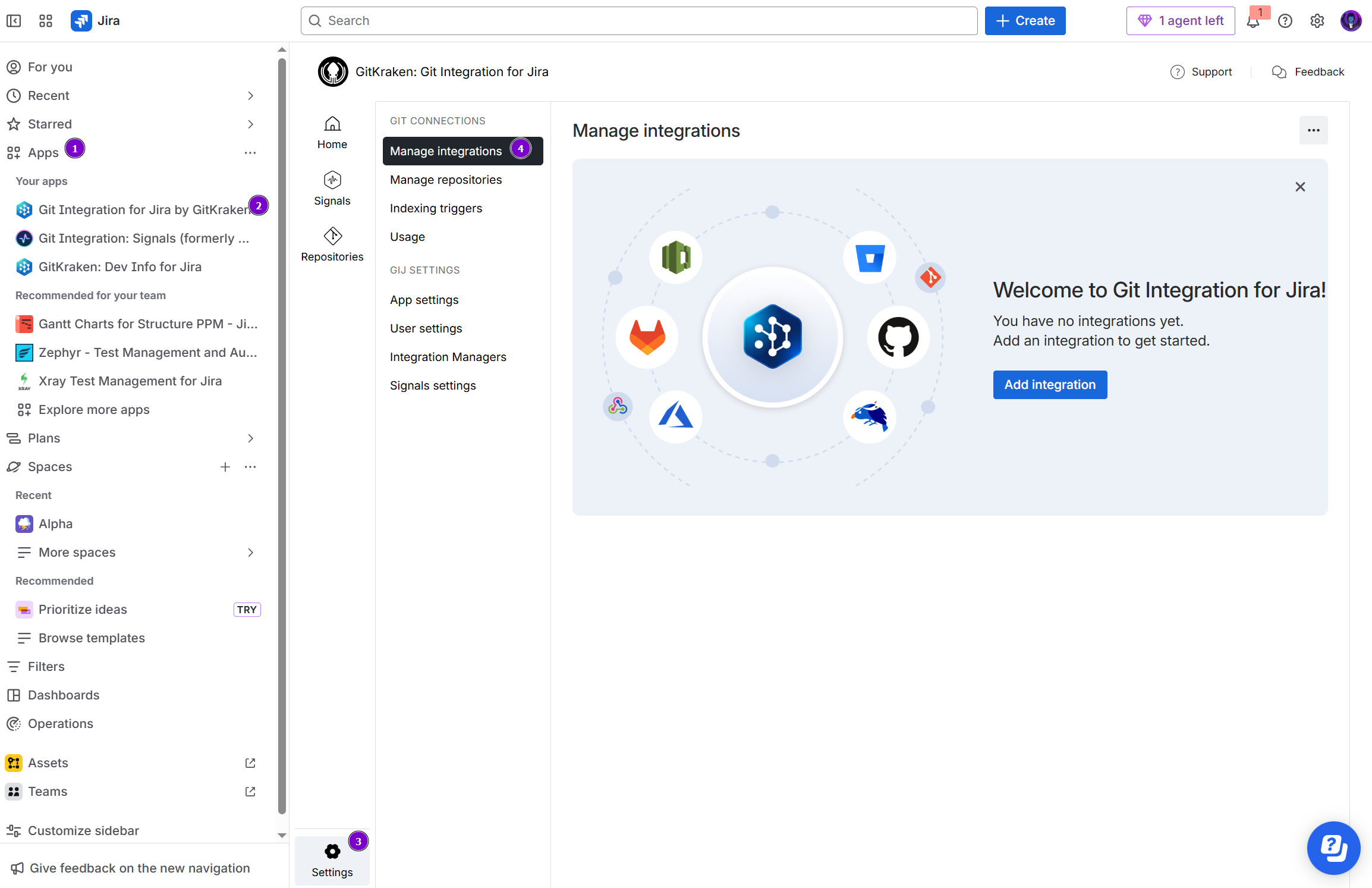
-
On the Manage integrations page, click Add integration.

-
For the following screen, click Team Foundation Server (TFS) to start integration with this git service. If you’re using Azure DevOps Server, choose that instead.
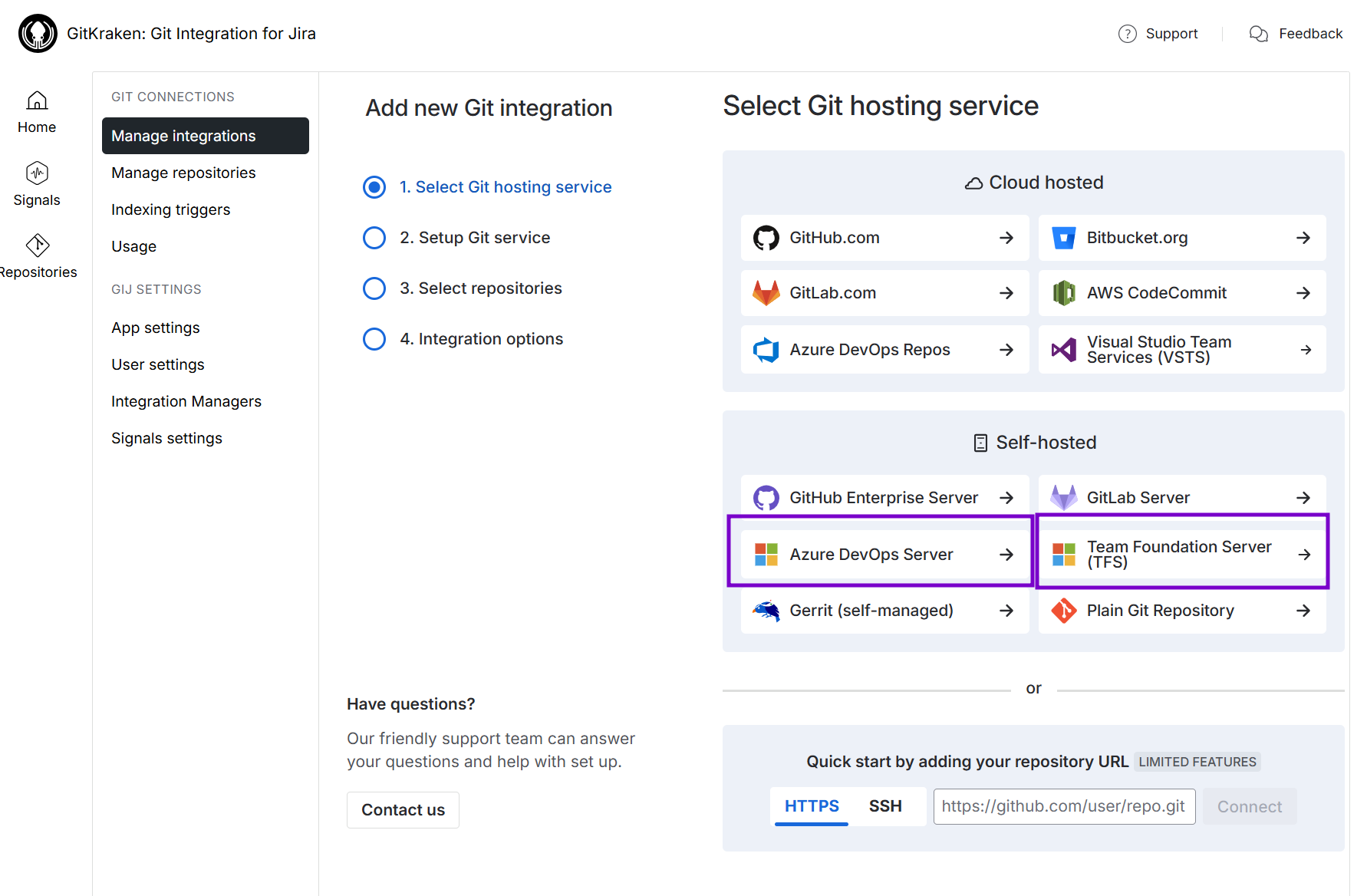
-
The following screen is displayed.
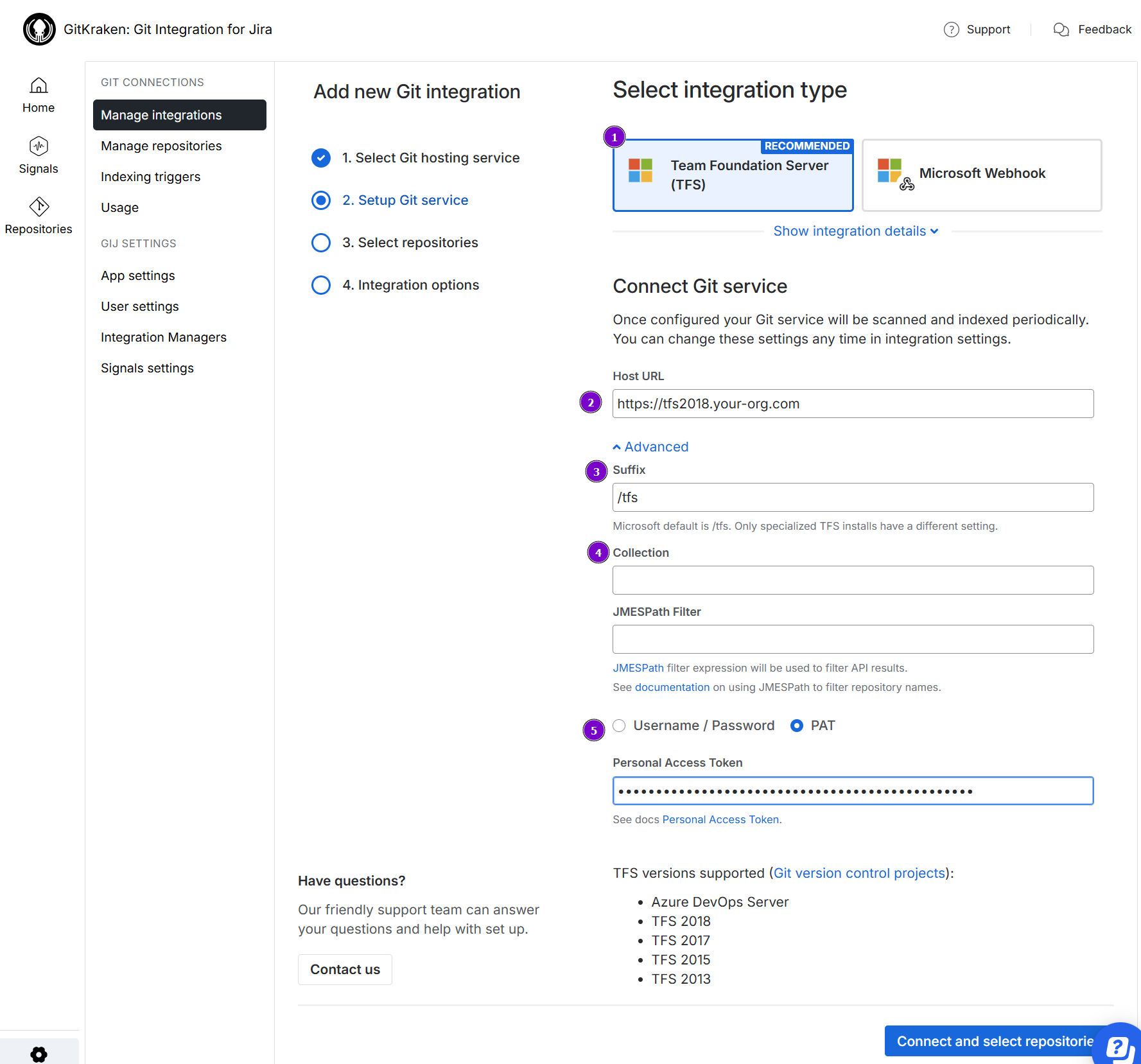
1. Choose **Team Foundation Server** for the integration type (recommended). If you are using **Azure DevOps Server**, choose that instead. 2. Enter the **Host URL** for your Azure DevOps/TFS git server. 3. **Suffix** – This is a relative path that defaults to `"/tfs"`. * For TFS integrations, the suffix will have a **/tfs** as default path. Thus, there is no need to add the `/tfs` to the **Host URL** path. If this field is blank, the Git Integration for Jira app automatically appends the default `"/tfs"` suffix and scans for all the collections inside it. * If this field is not empty, the app assumes it as a single collection path and will try to use it. * <b style='background-color:#DEEAFE; padding:1px 5px; color:#0C42A3; border-radius:3px; margin: 0 5px; font-size: small;'>AZURE DEVOPS SERVER</b> For Azure DevOps Server integrations, leave this field empty. 4. **Collection** – Enter a specific collection to use. If you know your specific collection, type its name in the provided box. The Git Integration app defaults to read and import all collection from the connected Azure DevOps Server/TFS server. 5. <b style='background-color:#FFF1B6; padding:1px 5px; color:#172A4C; border-radius:3px; margin: 0 5px; font-size: small;'>IMPORTANT</b> For TFS 2017 and newer, use <b>PAT</b> for authentication. Otherwise, use <b>Username/Password</b> for authentication (for example: TFS 2013/2015). PATs were introduced with TFS 2017 and newer. TFS 2013 and TFS 2015 do not support PATs. ```java IMPORTANT! ========== Do NOT include the <DOMAIN> in the Username field when Azure DevOps Server/TFS is connected to Active Directory. Example: "BigBrassBand\johnsmith" ==> "johnsmith" ```- Make sure to configure your PAT according to these articles: Team Foundation Server or Azure DevOps Server — especially the setting for Organization which must be set to All accessible organizations.
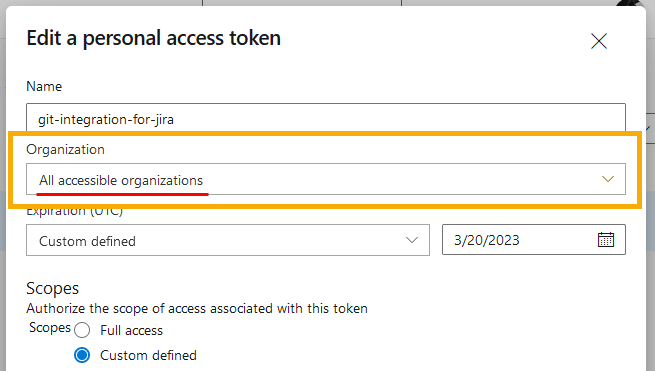
-
Configuring the Advanced settings is optional. However, admins/power users may set how the project listing is displayed by configuring the following options:
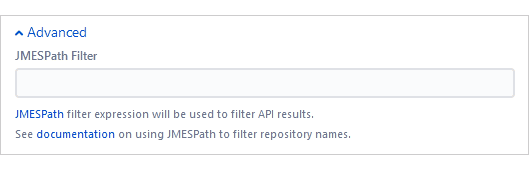
These settings are used with integration to control which tracked repositories are displayed and listed. Set a filter that will only load some cloned repositories which can be viewed via the Manage repositories page.
-
JMESPath filter – JMESPath is a query language for JSON used to filter API results and to limit which repositories are integrated. The maximum allowed length is 2000 characters or less.
-
If the field is empty, the Git Integration for Jira app will get all available accounts and then scans all available git repositories.
-
If the field is not blank, the app will assume it as a single account path and will try to use it. To connect to all available accounts, manually create integrations for each one of them.
Read about JMESPath expressions on their website. For help with writing expressions, please contact support.
To learn more examples, see article Jira Cloud: Working with JMESPath Filters. -
-
-
After filling up required fields, click Connect and select repositories to continue. The Git Integration for Jira app will read all available repositories from Azure DevOps Server/TFS.

- Currently, all available accounts are scanned and corresponding URLs are created internally. Repositories of the logged-in Microsoft user can be automatically connected to Jira Cloud. Repositories that are added or removed from Azure DevOps Server/TFS will be likewise connected or disconnected from Jira Cloud.
-
Click Connect repositories to complete this setup.
For now, only git projects are supported from Azure DevOps Server/TFS.
Azure DevOps Server/TFS git repositories are now connected to Jira Cloud.
Single git repository integration
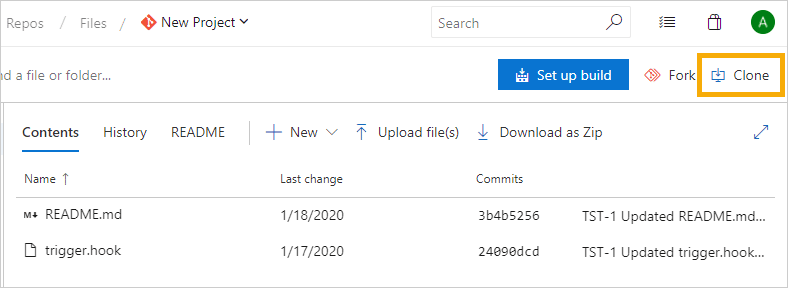
This process requires an existing Azure DevOps Server/TFS git repository. Look for the repository git clone URL on the repository project page. Choose between SSH or HTTPS.
Use this information to connect the Azure DevOps Server/TFS git repository to your Jira Cloud via Git Integration for Jira app:
Single git repository integration (HTTPS)
Single git repository integration (SSH)
The repository is now connected to Jira Cloud.
Troubleshooting integration
Some repositories are not showing for the integration user. If this is the case, make adjustments to the configuration on the following settings:
-
Permissions – verify correct permissions have been granted to the integration user.
-
Grant access to the Git Integration for Jira app.
-
Convert the current repository format to git.
For detailed information, see Troubleshooting: Repositories missing from Azure/VSTS/TFS integrations.
Webhooks and web linking
The Git Integration for Jira app automatically configures web linking for Azure DevOps Server/TFS git repositories.
First – configure webhooks in the Git Integration app in Jira via the Apps menu ➜ Git Integration: Manage integrations then click Indexing triggers (sidebar). Enable the feature and save the settings. Then follow these instructions to setup the webhook trigger. Azure DevOps Server/TFS webhooks will trigger an immediate index of all repositories within the integration.
For detailed step-by-step guide showcasing webhooks setup, see this article.
Linking Azure DevOps Server/TFS git commits to Jira Cloud
For the following steps, a Azure DevOps Server/TFS and a Visual Studio environment that supports git is required.
-
Open Visual Studio IDE. Sign in to your Microsoft account, if prompted.
-
Connect to your Azure DevOps Server/Team Foundation Server.
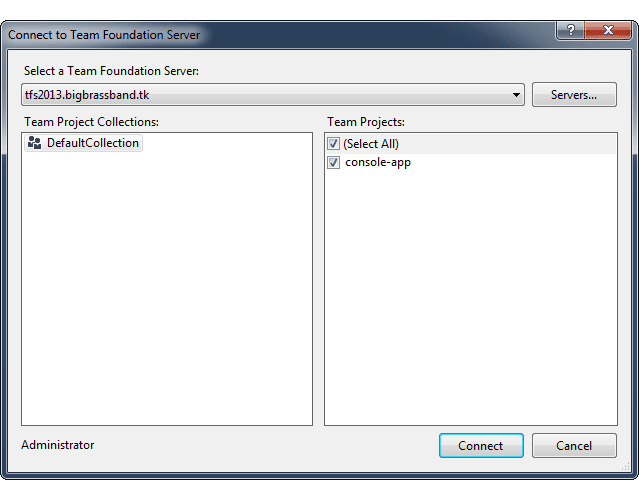
-
Select a server in the dropdown list to connect to.
-
If this is a new connection, add a new server by clicking Servers… :
-
Type your Azure DevOps Server/TFS server Host URL
-
Enter Username and Password, if prompted.
-
-
Click OK to continue.
-
-
Select a Team Project to work on then click Connect.
- For first time connection to the Azure DevOps Server/TFS team project, the default work branch is master.
-
On the Team Explorer, click Unsynced Commits or Sync.
-
Click the Pull to clone the git repositories to your local machine.
-
Make changes to the code of a file/project.
-
On the Team Explorer, click Changes.
-
Type a message for this commit.
To associate this commit to the Jira issue page, mention the Jira issue key along with the commit message. For example: PRJ-123 Fix null code Where PRJ-123 is the Jira issue key and Fix null code is the commit comment.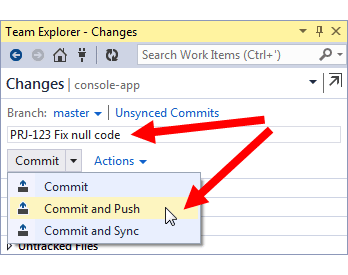
-
Click Commit and Push.
The commit is published to the Azure DevOps Server/TFS. To view the commit in Jira, go to the Jira issue mentioned in the commit message. Click the Git Commits tab in the Activity row.
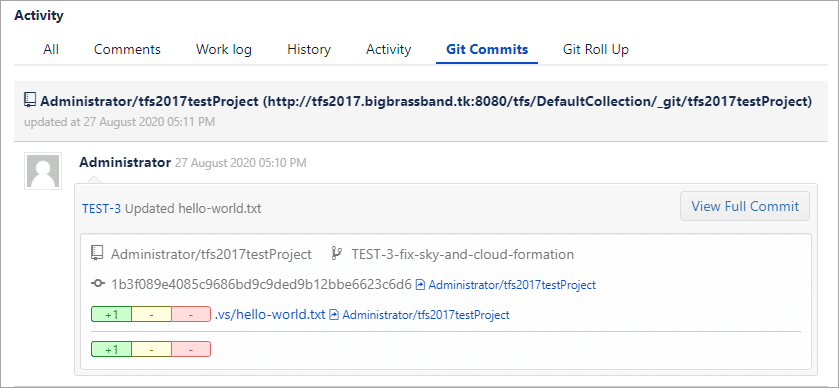
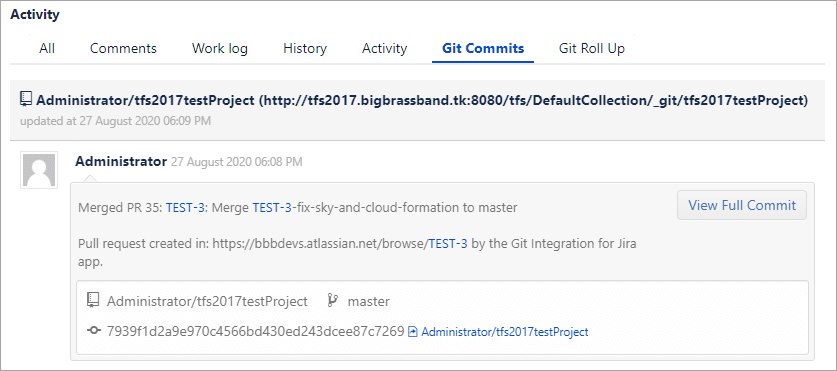
Viewing git commits in Jira Cloud
-
Perform a git commit by adding the Jira issue key in the commit message. This will associate the commit to the mentioned Jira issue.
-
Open the Jira issue.
-
Scroll down to the Activity panel then click the Git Commits tab.
-
Click View full commit to view the code diff.
For more information about this feature, see Documentation: Linking git commits to Jira issues.
Working with branches and pull requests with Azure DevOps Server/TFS
This process requires a Azure DevOps Server/TFS git repository and a PAT with at least Code (read and write) scope.
This feature allows users to create branches and pull requests while inside Jira.
Default branch
Most git integrations allow changing of the default branch of the repository/project other than “master”. This change is reflected in the Repository Settings of the Git Integration for Jira app on the next reindex. Full feature integrations support this function where Git Integration for Jira app gets the default branch from almost all integrations and apply this setting at repository level.
Creating branches
On your Jira Cloud, open a Jira issue. On the Jira Git integration development panel, click Open Git Integration then click Create branch. The following dialog is displayed.
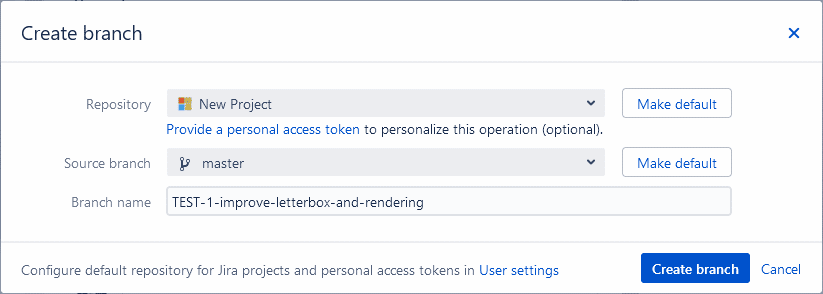
Pointers:
-
Select a Repository from the list.
-
The git host service logo is displayed for all the repositories in the dropdown list to easily identify which git service they belong.
-
If there are several repositories with the same name, the listed Azure DevOps Server/TFS repositories will have their names attached with a Azure DevOps Server/TFS organization name. For example,
johnsmith/second-webhook-test-repo. -
Use the search box in the dropdown list to filter displayed repositories.
-
OPTIONAL Designate the repository to be the default selected repository for current Jira project. To configure default repositories for more than one Jira project – use the User settings page.
-
For integration that uses PAT, the user is required to provide a personal access token for the repository to proceed creating the branch. Otherwise, no branch is created.
-
-
Choose a Source branch. OPTIONAL Designate the branch to be the default selected branch for the currently selected repository. To configure default branches for more than one repository – use the User settings page.
-
Enter a Branch name or leave it as is (recommended).
-
Click Create branch to complete this process.
The branch is created and can be viewed under the Branches tab in your Azure DevOps Server/TFS.
ON, the users will not be able to create/delete branches and pull requests.

To update the branch list to your Visual Studio’s Team Explorer:
-
Perform a Pull action on the connected team project. The branches list in your VS IDE should be updated now.
-
On the VS IDE Team Explorer, click Branches.
-
Click New Branch then select the newly-created branch from the dropdown list.
-
Click Create Branch. The selected branch is now listed under the Published Branches in the Team Explorer.
-
Make changes to a file or project then perform a commit to the selected branch.

-
On the Team Explorer, click Changes.
-
Make sure that Branch: displays the name of the newly-created branch. If not, select it again from the list.
-
This will associate the commit to the mentioned Jira issue key.
-
-
Click the dropdown on the Commit button then select Commit and Push.
The commit is pushed to the new branch and is now ready for merge.
Creating pull requests
The pull request feature works the same as merge request.
On your Jira Cloud, open the Jira issue where your previously created a branch. On the developer panel under Git integration, click Create pull request. The following dialog is displayed.

Pointers:
-
Select a Repository from the list.
-
The selected repository will display the git service logo to identify which git host it is located from.
-
If there are several repositories with the same name, the listed Azure DevOps Server/TFSrepositories will have their names attached with a owner/team name. For example,
johnsmith/second-webhook-test-repo. -
Use the search box to look for the specific repository that will be used.
-
OPTIONAL Designate the repository to be the default selected repository for current Jira project. To configure default repositories for more than one Jira project – use the User settings page.
-
For integration that uses PAT, the user is required to provide a personal access token for the repository to proceed creating the branch. Otherwise, no branch is created.
-
-
Choose the newly-created branch as the Source branch. OPTIONAL Designate the branch to be the default selected branch for the currently selected repository. To configure default branches for more than one repository – use the User settings page.
-
Set master as the Target branch.
-
Enter a descriptive Title or leave it as is (recommended).
The branch and the pull request status are displayed on the developer panel.
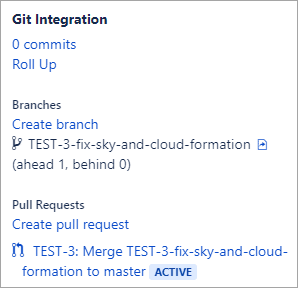
The pull request is also listed in the Azure DevOps Server/TFS.
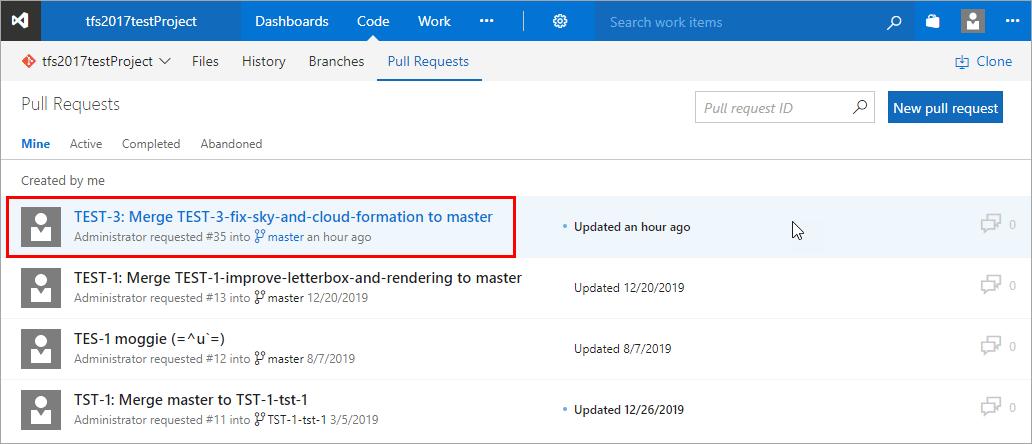
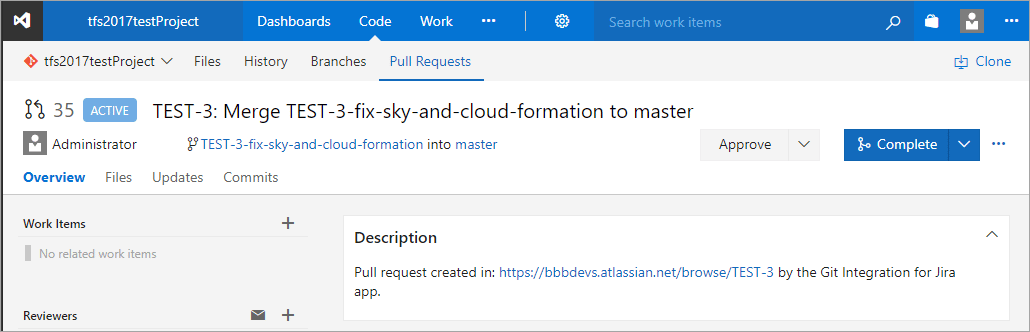
Merging branch to master
Continuing from the above steps, the current branch is ready for merge.
-
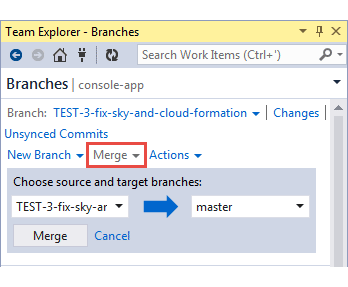
On your VS IDE Team Explorer, go to Branches.
-
Click the Merge tab.
-
Set the source to the branch you pushed the commits to.
-
Set the target branch to master.
-
-
Click the Merge button to continue.
The reviewer’s approval is required to completely merge the pull request. This usually takes place in the Azure DevOps Server/TFS web UI where your updated code is being reviewed.
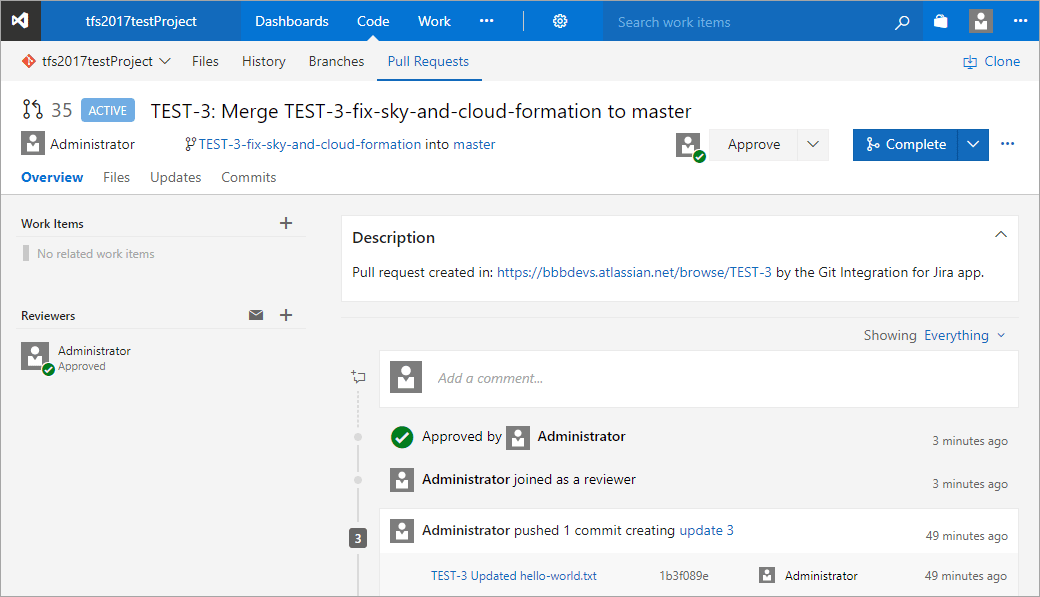
Once approved, the team leader or reviewer can then complete the merge. The commit can be viewed in the associated Jira issue page.
More Integration Guides
GitHub.com (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
GitHub Enterprise Server (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
GitLab.com (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
GitLab CE/EE (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
Azure DevOps | Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
Azure DevOps Server | Team Foundation Services (this page)
AWS CodeCommit (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
Gerrit (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
Bitbucket Cloud (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
Introduction to Git integration (Git Integration for Jira Cloud)
Last updated: December 2025